Fil:GCD through successive subtractions.svg

Fuld opløsning (SVG fil, basisstørrelse 660 × 825 pixels, filstørrelse: 5 KB)
|
|
Denne fil er fra Wikimedia Commons. Beskrivelsen af filen fra Commons er gengivet nedenfor. |
Beskrivelse
| BeskrivelseGCD through successive subtractions.svg |
English: The set of common divisors of two given natural numbers is the set of divisors of one and only one natural number, called the “greatest common divisor” of the initial pair. To prove its existence, it is sufficient to exhibit we can always calculate it, from any pair of natural numbers. How to understand “greatest”? The order in question is divisibility: a partial order on set ℕ of natural numbers. For example, 2 is a common divisor
 that can be written: that can be written:  We will soon calculate the greatest common divisor We will soon calculate the greatest common divisor   Zero is multiple of any natural number, in other words, zero is the greatest element of ℕ for divisibility. Zero is multiple of any natural number, in other words, zero is the greatest element of ℕ for divisibility.  is not the greatest natural number for the usual order relation, of which the symbol is not the greatest natural number for the usual order relation, of which the symbol  The least element of ℕ for divisibility is 1. The least element of ℕ for divisibility is 1.
Under the algorithm of the image, Instead of replacing A novice in coding can copy and paste in a window dedicated to JavaScript one of the following comparisons, and then command the execution: /* To open a Firefox window
dedicated to JavaScript code: Shift + F4 */
d = r = k = 182; p = 238; // example of input values,
// that we can replace with two other natural numbers
if( s = p){ // if the common value of s and p is not zero
while(r){ // while the value of r is not zero
if(r < s){ // in this case, reverse the values of r and s
d = s; s = r; r = d }
r = r-s } // end of the loop 'while(r)'
d = s } // end of the block that begins with 'if( s = p)'
" GCD("+ k +", "+ p +") = "+ d; // output: a String object
// Keyboard shortcut in Firefox to execute the code: Ctrl + L
On the image top, try{ // in case of error in this block,
// execution failure of this code block, go to 'catch'
d = r = k = 408; p = 255; // example of input values
var b; // global scope declaration
s = function(n){
// to test the value of parameter n: is it a natural number?
b = n.constructor == Number; // Boolean value
if( !b // first incorrect case
|| n < 0 || n != Math.floor(n) // other incorrect cases
) throw n
// in one of the previous cases, n is thrown as error
}; // end of assignment to variable s
s(k); s(p); // verifications
if( s = p){ // if the common value of s and p is not zero
while(r){
if(r < s){d = s; s = r; r = d} r = r-s } d = s }
" GCD("+ k +", "+ p +") = "+ d
}catch(e){ // in case of error (if e is thrown)
" "+( b ? e +" is not a natural number.":
" Incorrect code.")
}
   is the irreducible form is the irreducible form  Two natural numbers of which the GCD is 1 are called coprime integers. Two natural numbers of which the GCD is 1 are called coprime integers.Français : Voir la version en français… |
| Dato | |
| Kilde | Eget arbejde |
| Forfatter | Arthur Baelde |
| Andre versioner |
|
| SVG udvikling InfoField | This /Baelde was created with a text editor. |
Licensering
- Du må frit:
- at dele – at kopiere, distribuere og overføre værket
- at remixe – at tilpasse værket
- Under følgende vilkår:
- kreditering – Du skal give passende kreditering, angive et link til licensen, og oplyse om der er foretaget ændringer. Du må gøre det på enhver fornuftig måde, men ikke på en måde der antyder at licensgiveren godkender dig eller din anvendelse.
- deling på samme vilkår – Hvis du bearbejder, ændrer eller bygger videre på dette værk, skal du distribuere dine bidrag under den samme eller en kompatibel licens som originalen.
Captions
Elementer som er med i denne fil
afbilder
Denne egenskab har en værdi, men den er ukendt
27. juni 2018
Filhistorik
Klik på en dato/tid for at se filen som den så ud på det tidspunkt.
| Dato/tid | Miniaturebillede | Dimensioner | Bruger | Kommentar | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| nuværende | 26. apr. 2024, 15:12 | 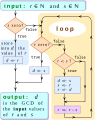 | 660 × 825 (5 KB) | Arthur Baelde | more legible |
| 27. jun. 2018, 11:06 |  | 660 × 825 (5 KB) | Arthur Baelde | User created page with UploadWizard |
Filanvendelse
Der er ingen sider der bruger denne fil.
Global filanvendelse
Følgende andre wikier anvender denne fil:
- Anvendelser på bo.wikipedia.org
- Anvendelser på en.wikipedia.org
- Anvendelser på jv.wikipedia.org
Metadata
Denne fil indeholder ekstra information, som formentlig er tilføjet fra et digitalt kamera eller en skanner, der enten blev brugt til at skabe billede eller digitalisere det. Hvis filen har været ændret siden dens oprindelige tilblivelse, kan nogle detaljer muligvis ikke fuldt ud repræsentere det modificerede billede.
| Bredde | 660 |
|---|---|
| Højde | 825 |





























