Bruger:Nis Hoff/Kladde5: Forskelle mellem versioner
Nis Hoff (diskussion | bidrag) Tømmer siden for indhold |
Nis Hoff (diskussion | bidrag) No edit summary |
||
| Linje 1: | Linje 1: | ||
{{Militær konflikt |
|||
|konflikt = Østfronten under 2. Verdenskrig |
|||
|delaf= [[2. Verdenskrig]] |
|||
|billede=[[Image:Soviet flag on the Reichstag roof Khaldei.jpg|300px]] |
|||
|titel=Sovjetiske soldater hejser det sovjetiske flag over Reichtags bygning i Berlin under slaget om Berlin, maj 1945 |
|||
|dato=[[21. juni]] [[1941]] - [[8. maj]] [[1945]] |
|||
|sted= [[Centraleuropa|Central-]] og [[Østeuropa]] |
|||
|casus= |
|||
|territorie= Sovjetunionen erobrer Østpreussen og de østeuropæiske lande bliver sovjetiske lydstater med kommunistisk styre. |
|||
|resultat= Afgørende sovjetisk sejr |
|||
|part1= [[Billede:Flag of the Soviet Union.svg|22px|border]] [[Josef Stalin]] |
|||
{{flagikon|USSR}} '''[[Soviet Union]]'''<ref name=Allied-help>Sovjetunionen rekrutterede også nogle udenlandske enheder (Tjekkoslovakiske og Rumænske). Sovjetunionen fik også hjælp fra USA og Storbritannien. Hertil kom i mindre omfang støtte fra [[Polen]], [[Rumænien]] (fra 1944), [[Bulgarien]] (fra 1944) og [[Tjekkoslovakiet]]</ref><br> |
|||
{{flagicon image|Flaga PPP.svg}} [[Polish Underground State]]<br> |
|||
{{flagikon|POL}} [[Polish Committee of National Liberation]]<br> |
|||
{{flagikon|ROM}} [[Rumænien]] (fra 1944)<br> |
|||
{{flagicon image|Flag of the Bulgarian Homeland Front.svg}} [[Bulgarien]] (fra 1944)<br>{{flagikon|FIN}} [[Finland]] (fra 1944)<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|Czechoslovakia}} [[Czechoslovak military units on Eastern front|Czechoslovak Republic]]</small> |
|||
|fører1 ={{flagicon|USSR|1923}} '''[[Joseph Stalin]]'''<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Aleksei Antonov]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Nikandr Chibisov]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Ivan Konev]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Rodion Malinovsky]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Hovhannes Bagramyan|Ivan Bagramyan]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Ivan Fedyuninsky]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Valerian Frolov]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Vasiliy Gordov]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Leonid Govorov]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Mikhail Kirponos]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Mikhail Khozin]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Fyodor Kuznetsov]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Ivan Maslennikov]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Kirill Meretskov]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Ivan Petrov (General)|Ivan Petrov]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Markian Popov]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Maxim Purkayev]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Alexander Rodimtsev]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Konstantin Rokossovsky]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Pavel Rotmistrov]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Vasiliy Sokolovsky]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Semyon Timoshenko]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Fyodor Tolbukhin]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Aleksandr Vasilevsky]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Nikolai Fyodorovich Vatutin|Nikolai Vatutin]]<br>{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Kliment Voroshilov]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Andrei Yeremenko]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Matvei Zakharov]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|USSR|1923}} [[Georgy Zhukov]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon image|Flaga PPP.svg}} [[Tadeusz Bór-Komorowski]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|Poland}} [[Zygmunt Berling]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|Poland}} [[Michał Żymierski]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|Poland}} [[Karol Świerczewski]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|Czechoslovakia}} [[Ludvík Svoboda]] |
|||
|styrke1= |
|||
|tab1=''See [[Eastern Front (World War II)#Casualties|below]]'' |
|||
|part2= {{Land|flagland|Nazityskland}}<ref name=Axis-help>Germany's allies, in total, provided a significant number of troops and material to the front. There were also numerous foreign units recruited by Germany, notably the [[Russian Liberation Army]] and the [[Blue Division|Spanish Blue Division]].</ref><small> |
|||
{{flagicon|Romania}} [[Romania during World War II|Romania]] (to 1944) <br> {{flagicon|Finland}} [[Military history of Finland during World War II|Finland]] (to 1944)<br>{{flagicon|Hungary|1940}} [[Hungary during World War II|Hungary]]<br>{{flagicon|Italy|1861-state}} [[Italian war in Soviet Union, 1941-1943|Italy]] (to 1943)<br>{{flagicon|Slovakia|1938}} [[Slovak Republic (1939–1945)|Slovakia]]<br>{{flagicon|Croatia|1941}} [[Independent State of Croatia|Croatia]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|Bulgaria}} [[Military history of Bulgaria during World War II|Bulgaria]] (September 5-8, 1944)<br> |
|||
[[Collaboration during World War II#Partial list of collaborationist organizations|Volunteers]] |
|||
|fører2 = {{flagicon|Germany|Nazi}} '''[[Adolf Hitler]]''' <br> |
|||
{{flagicon|Germany|Nazi}} [[Ernst Busch (military)|Ernst Busch]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|Germany|Nazi}} [[Heinz Guderian]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|Germany|Nazi}} [[Paul Ludwig Ewald von Kleist|Ewald von Kleist]]<br>{{flagicon|Germany|Nazi}} [[Günther von Kluge]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|Germany|Nazi}} [[Georg von Küchler]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|Germany|Nazi}} [[Wilhelm Ritter von Leeb]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|Germany|Nazi}} [[Wilhelm List]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|Germany|Nazi}} [[Erich von Manstein]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|Germany|Nazi}} [[Walter Model]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|Germany|Nazi}} [[Friedrich Paulus]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|Germany|Nazi}} [[Gerd von Rundstedt]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|Germany|Nazi}} [[Ferdinand Schörner]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|Germany|Nazi}} [[Erhard Raus]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|Germany|Nazi}} [[Walther von Reichenau]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|Romania}} [[Ion Antonescu]] <br> |
|||
{{flagicon|Romania}} [[Petre Dumitrescu]], [[Third Army (Romania)|3rd Army]]<br>{{flagicon|Romania}} [[Constantin Constantinescu]], [[Fourth Army (Romania)|4th Army]]<br>{{flagicon|Finland}} [[Karl Lennart Oesch]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|Finland}} [[Carl Gustaf Emil Mannerheim]] <br> |
|||
{{flagicon|Hungary|1940}} [[Gusztáv Vitéz Jány]], [[Hungarian Second Army|2nd Army]]<br>{{flagicon|Hungary|1940}} [[Ferenc Szombathelyi]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|Italy|1861-state}} [[Giovanni Messe]], [[Italian war in Soviet Union, 1941-1943|CSIR]]<br> |
|||
{{flagicon|Italy|1861-state}} [[Italo Gariboldi]], [[Italian war in Soviet Union, 1941-1943|ARMIR]]<br> |
|||
|styrke2= |
|||
|tab2=''See [[Eastern Front (World War II)#Casualties|below]]'' |
|||
|noter= |
|||
}} |
|||
The '''Eastern Front of World War II''' ({{lang-de|die Ostfront 1941-1945}} <ref>{{de icon}} [http://www.russlandfeldzug.de/ Die Ostfront 1941-1945]</ref>, ''der Rußlandfeldzug 1941-1945'' (Russian campaign) or ''der Ostfeldzug 1941-1945'' (Eastern Campaign)<ref>{{de icon}} [http://www.balsi.de/Weltkrieg/Verlauf/Russland/Russland-Startseite.htm Der Rußlandfeldzug]; {{de icon}} [http://www.torweihe.de/ 2. Weltkrieg]</ref>) was a [[Theatre (warfare)|theatre of war]] between the [[German Reich]] and the [[Soviet Union]] which encompassed [[Central Europe|central]] and [[eastern Europe]] from [[June 22]], [[1941]] to [[May 9]], [[1945]]. Nazi propaganda dubbed the conflict '''The Crusade against Bolshevism'''. In all Soviet and the majority of [[Russian language|Russian]] sources, the conflict in Eastern Europe is referred to as the '''[[Great Patriotic War (term)|Great Patriotic War]]''', but sometimes that phrase also includes operations against Japan in 1945. Some scholars of the conflict use the term '''Russo-German War''', while others use '''Soviet-German War''', '''Nazi-Soviet War''', '''German-Soviet War''', or '''Axis-Soviet War'''. |
|||
It was the largest theatre of war in history and was notorious for its unprecedented ferocity, destruction, and immense loss of life. It bore the bulk of the [[Holocaust]], and stands unparalleled in terms of the volume of scholarly analysis and cultural depictions it generated (films, books, video games etc.). More people fought and died on the Eastern Front than in all other theatres of [[World War II]] combined. With over 30 million dead, many of them civilians, the Eastern Front has been called a [[Genocide|war of extermination]]. It resulted in the destruction of the [[Third Reich]], the [[partition of Germany]] and the rise of the Soviet Union as a military and industrial [[superpower]]. |
|||
The series of events preceding the opening of the Eastern Front included the [[invasion of Poland]] in 1939 by [[Nazi Germany]] and the resulting fourth partition of [[Poland]] when the Soviet Union used the invasion as a pretext to annex the eastern regions of the country, populated mostly by [[History of Poland (1918–1939)|Ukrainians and Belarussians]], as outlined in the secret codicil to the August 1939 [[Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact|Soviet-German non-aggression pact]], which also paved the way for the 1940 [[Occupation of Baltic states]] and the [[Soviet occupation of Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina|occupation of Bessarabia]]. |
|||
This article, however, concentrates on the much larger conflict fought from June 1941 to May 1945, in which the two principal belligerent powers were Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union. The Soviet-Finnish [[Continuation War]] may be considered the northern flank of the Eastern Front. In addition, the joint [[Operation Silver Fox|German-Finnish operations]] across the northernmost Finnish-Soviet border and in the [[Murmansk Oblast|Murmansk region]] are considered part of the Eastern Front. |
|||
==Forces== |
|||
The war was fought between the German Reich, its allies, and many pro-Nazi volunteers from occupied states, against the Soviet Union, and eventually its allies of the [[British Commonwealth]], France and the United States. The conflict began on [[22 June]] [[1941]] as part of the [[Operation Barbarossa]] Offensive, when [[Axis powers|Axis]] forces crossed the borders, described in the [[German-Soviet Nonaggression Pact]], thereby invading the Soviet Union. The war ended on [[9 May]] [[1945]], when [[Wehrmacht|Germany's armed forces]] [[Unconditional surrender|surrendered unconditionally]] following the [[Berlin Offensive]], a strategic operation executed by the [[Red Army]], also known as the [[Battle of Berlin]]. |
|||
The states that provided forces and other resources for the German war effort included the [[Axis Powers]] — foremost [[Italy]], [[Romania]], [[Hungary]], and pro-Nazi [[Slovakia]] and [[Croatia]]. The [[anti-Soviet]] [[Finland]], which had fought two conflicts with the Soviet Union, also joined the Offensive. The Wehrmacht forces were also assisted by anti-[[Communist]] [[Partisan (military)|partisans]] in places like [[Western Ukraine]], the [[Baltic states]] and later [[Crimean Tatars]]. Among the most prominent volunteer army formations was the [[Blue Division|Spanish Blue Division]], sent by Spanish dictator [[Francisco Franco]] to keep his ties to the Axis intact. <br /> |
|||
The Soviet Union offered support to the partisans in many Wehrmacht-occupied countries in [[Eastern Europe]], notably those in Slovakia, Poland and the [[Kingdom of Yugoslavia]]. In addition the [[Polish Armed Forces in the East]], particularly the [[Polish First Army|First]] and [[Polish Second Army|Second]] Polish armies, were armed and trained, and would eventually fight alongside the [[Red Army]]. The [[Free French]] forces also contributed to the Red Army by formation of [[Normandie-Niemen|GC3]] (''Groupe de Chasse 3'' or 3rd Fighter Group) unit to fulfill the commitment of [[Charles de Gaulle]], leader of the Free French, who thought that it was important for French servicemen to serve on all fronts. |
|||
British and Commonwealth forces contributed directly to the fighting on the Eastern Front through their service in the [[Arctic convoys of World War II|convoys]] and training Red Air Force pilots, as well as in provision of early materiel and intelligence support. The later massive materiel support of the [[Lend-Lease]] by the United States and Canada played a significant part particularly in the [[logistics]] of the war. |
|||
==Ideologies== |
|||
{{main|Timeline of events preceding World War II}} |
|||
[[Adolf Hitler]] had argued in his autobiography ''[[Mein Kampf]]'' for the necessity of [[Lebensraum]], acquiring new territory for German settlement in Eastern Europe. He envisaged settling Germans there as a master race, while deporting most of the inhabitants to [[Siberia]] and using the remainder as [[slave labour]]. |
|||
To hard line Nazis in Berlin, (like Himmler<ref> |
|||
{{cite web |
|||
|url = http://www.ess.uwe.ac.uk/genocide/SS2.htm |
|||
| title = Speech of the Reichsfuehrer-SS at the meeting of SS Major-Generals at Posen October 4th, 1943 |
|||
| author = Heinrich Himmler |
|||
| work = Source: Nazi Conspiracy and Aggression, Vol. IV. USGPO, Washington, 1946, pp.616-634 |
|||
| publisher = Stuart Stein , University of the West of England. |
|||
| quote = "Whether nations live in prosperity or starve to death . . . interests me only in so far as we need them as slaves for our Kultur. . . " |
|||
}}</ref>) the war against the Soviet Union was one of a struggle of [[Fascism]] against [[Communism]], and the [[Aryan race]] against the "[[Untermensch|inferior]]" [[Slavs|Slavic race]]. Hitler referred to it in unique terms, calling it a "war of annihilation", one in which the Soviet Union was to be utterly destroyed and the populations of Eastern Europe and Russia were to be enslaved and exterminated. This would further German expansion and provide for the colonization of Eastern Europe and Western Russia. The plan was called the [[Generalplan Ost]]. In addition, the Nazis also sought to wipe out the large [[Jewish]] population of Eastern Europe<ref> |
|||
{{cite web |
|||
|url=http://www.writing.upenn.edu/~afilreis/Holocaust/wansee-transcript.html |
|||
|accessdate=2009 1 5 |
|||
|title = The Wannsee Conference Protocol |
|||
|work = source: John Mendelsohn, ed., _The Holocaust: Selected Documents in Eighteen Volumes._ Vol. 11: The Wannsee Protocol |
|||
| publisher = Literature of the Holocaust, university of pennsylvania |
|||
|author = revisions to translation by Dan Rogers |
|||
}}</ref> as part of the [[Holocaust]]. |
|||
After [[Great Purge|the great purge]] of the 1930s, Hitler saw the Soviet Union as militarily weak and ripe for conquest: "We have only to kick in the door and the whole rotten structure will come crashing down."<ref>Speer, Albert. ''Inside the Third Reich.'' p. 238</ref> Thus, another short Blitzkrieg was expected, no serious preparations for warfare in winter, or prolonged over years, were made. In the aftermath of the [[Battle of Stalingrad]] in 1943 and the resulting dire German military situation, Hitler and Nazi propaganda proclaimed the war to be a German defense of European (Western) Civilization against destruction by the vast "[[Bolshevism|Bolshevik]] hordes" that were pouring into Europe. |
|||
[[Joseph Stalin]]'s vision also included the occupation of foreign countries: using the occasion of world attention drawn to the [[Western Front (World War II)|Western Front]], [[Occupation of Baltic States|Soviet Union occupied the three Baltic countries]] and [[Bessarabia]] in 1940, thus gaining a ''place d'arme'' in case of a possible war with Hitler-Germany. [[Soviet invasion of Poland (1939)|Soviet active participation in the 1939 invasion of Poland]] should also not be underestimated. |
|||
==Results== |
|||
The Eastern Front was by far the largest and bloodiest [[Theatre (warfare)|theatre]] of World War II. It is generally accepted as being the deadliest conflict in human history, with over 30 million killed as a result. It involved more land combat than all other World War II theatres combined. The distinctly brutal nature of warfare on the Eastern Front was exemplified by an often willful disregard for human life by both sides. It was also reflected in the ideological premise for the war, which also saw a momentous clash between two directly opposed and radical ideologies. |
|||
Aside from the ideological conflict, the mindframe of the leaders of Germany and the Soviet Union, Hitler and Stalin respectively, contributed to the escalation of terror and murder on an unprecedented scale. Stalin and Hitler both disregarded human life in order to achieve their goal of victory. This included terrorization of their own people, as well as [[mass deportation]] (planned, in the case of Germany) of entire populations. All these factors resulted in tremendous brutality both to combatants and civilians that found no parallel on the [[Western Front (World War II)|Western Front]]. According to the [[Time (magazine)|Time]]: '' "By measure of manpower, duration, territorial reach and casualties, the Eastern Front was as much as four times the scale of the conflict on the [[Western Front (World War II)|Western Front]] that opened with the [[Normandy invasion]]."''<ref>[http://www.time.com/time/world/article/0,8599,1809018,00.html Remembering a Red Flag Day - TIME<!-- Bot generated title -->]</ref> |
|||
The war inflicted huge losses and suffering upon the civilian populations of the affected countries. Behind the front lines, [[Wiktionary:atrocity|atrocities]] against civilians in German-occupied areas were routine, including the Holocaust. German and German-allied forces treated civilian populations with exceptional brutality, massacring villages and routinely killing civilian hostages. Both sides practiced widespread [[scorched earth]] tactics, but the loss of civilian lives in the case of Germany was incomparably smaller than that of the Soviet Union, in which at least 20 million civilians were killed by the Nazis. When the Red Army invaded Germany in 1944, many German civilians suffered from vengeance taken by Red Army soldiers (see [[Red Army atrocities]]). After the war, following the [[Yalta conference]] agreements between the Allies, the [[German people|German populations]] of [[East Prussia]] and [[Silesia]] were [[German exodus from Eastern Europe|displaced to the west]] of the [[Oder-Neisse Line]], in what became one of the largest [[forced migration]]s of people in world history. The German minority scattered over large swaths of Eastern Europe was thus expelled and those who did not manage to leave were exterminated. |
|||
Much of the combat took place in or close by populated areas, and the actions of both sides contributed to massive loss of civilian life as well as a tremendous material damage. According to a summary, presented by Lieutenant General Roman Rudenko at the [[Nuremberg Trials|International Military Tribunal]] in [[Nuremberg]], the property damage in the Soviet Union inflicted by the Axis invasion was estimated to a value of 679 billion rubles. The largest number of civilian deaths in a single city was 1.2 million citizens dead during the [[Siege of Leningrad]]. The combined damage consisted of complete or partial destruction of 1,710 cities and towns, 70,000 villages/hamlets, 2,508 church buildings, 31,850 industrial establishments, 40,000 miles of railroad, 4100 railroad stations, 40,000 hospitals, 84,000 schools, and 43,000 public libraries. Seven million horses, and 17 million sheep and goats were also slaughtered or driven off.<ref>''[[The New York Times]]'', [[February 9]], [[1946]], Volume 95, Number 32158.</ref>Wild fauna were also affected. Wolves and foxes fleeing westward from the killing zone, as the Russian army advanced 1943-45, were responsible for a [[rabies]] epidemic which spread slowly westwards, reaching the Channel coast in 1968.<ref>Chris Bellamy (2007) ''Absolute War: Soviet Russia in the Second World War''. London: Macmillan: 1-2</ref> |
|||
==Background== |
|||
===Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact=== |
|||
{{Main|Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact}} |
|||
The [[Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact|Molotov-Ribbentrop Non-Aggression Pact]] of August 1939 had established a [[Non aggression pact|non-aggression agreement]] between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union, and a secret [[Protocol (treaty)|protocol]] outlined how [[Finland]], [[Estonia]], [[Latvia]], [[Lithuania]], [[Poland]], and [[Romania]] would be divided between them. The two powers invaded and partitioned [[Invasion of Poland (1939)|Poland in 1939]]. In November 1939 the Soviet Union waged the [[Winter War]] against Finland. And in June 1940, threatening to use force if its demands were not fulfilled, it won the diplomatic wars against Romania and three [[Baltic states]] allowing it to peacefully [[occupation of the Baltic countries|occupy Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania]] ''[[de facto]]'' while no western state regarded the annexation of these states ''[[de jure]]''. The pact allowed for the return of the [[Ukraine|Ukrainian]], [[Belarus]]ian, and [[Moldavia]]n territories in the north and northeastern regions of Romania (Northern [[Bucovina]] and [[Basarabia]]) to the Soviet Union. |
|||
===The decision for war=== |
|||
{{main|Aufbau Ost (1940)|Lossberg study}} |
|||
For nearly two years the border was quiet while Germany conquered [[Operation Weserübung|Denmark, Norway]], [[Battle of France|France, The Low Countries]], and the [[Balkans Campaign|Balkans]]. Hitler had however always intended to renege on the pact with the Soviet Union and invade, and appears to have made the decision of when to do so in the spring 1940. Hitler believed that the Soviets would quickly capitulate after an overwhelming German offensive and that the war could largely end before the onset of the fierce Russian winter. |
|||
Some say [[Joseph Stalin]] was fearful of war with Germany or just did not expect Germany to start a [[two-front war]], and was reluctant to do anything to provoke Hitler. Others say that Stalin was eager for Germany to be at war with other capitalist countries. Another viewpoint is that Stalin expected war in 1942 (the time when all his preparations would be complete) and stubbornly refused to believe its early arrival.<ref>[Hardesty, Von. ''Red Phoenix: The Rise of Soviet Air Power 1941-1945.'' p. 16, Smithsonian Institution Press. ISBN 1-56098-071-0]</ref> |
|||
British historians Alan S. Milward and W. Medicott show that Nazi Germany--unlike Imperial Germany--was prepared for only a short-term war (Blitzkrieg).{{Fact|date=June 2008}} According to Andreas Hillgruber, without the necessary supplies from the USSR and the strategic security in the East, Germany could not have succeeded in the West. Had the Soviets joined the Anglo-French blockade, the German war economy would have been starved. With its own raw materials in September 1939, Germany could have been supplied for a mere 9 to 12 months.{{Fact|date=June 2008}} |
|||
Even though Germany had been assembling very large numbers of troops in eastern Poland and making repeated [[reconnaissance]] flights over the border, Stalin ignored the warnings of his own as well as foreign intelligence. Moreover, on the very night of the invasion, Soviet troops received a directive undersigned by [[Marshal]] [[Semyon Timoshenko]] and [[General of the Army]] [[Georgy Zhukov]] that ordered (as demanded by Stalin): "do not answer to any provocations" and "do not undertake any actions without specific orders". The German invasion therefore caught the Soviet military and leadership largely by surprise, even though Stalin did receive a message from his intelligence detailing information on the attack. |
|||
For Soviet preparations, see [[Operation Barbarossa#Soviet preparations|Operation Barbarossa: Soviet preparations]]. |
|||
==Conduct of operations== |
|||
{{main|Strategic operations of the Red Army in World War II}} |
|||
While German historians do not apply any specific periodisation to the conduct of operations on the Eastern Front, all Soviet and Russian historians divide the war against Germany and its allies into three periods, which are further subdivided into the major [[Military campaign|Campaign]]s of the [[Theatre of war]]:<br /> |
|||
1. '''[[First period of World War II]]''' ({{lang-ru|Первый период Великой Отечественной войны}}) (22 June 1941 - 18 November 1942)<br /> |
|||
* Summer-Autumn Campaign ({{lang-ru|Летне-осенняя кампания 1941 г.}}) (22 June - 4 December 1941) |
|||
* Winter Campaign of 1941-42 ({{lang-ru|Зимняя кампания 1941/42 г.}}) (5 December 1941 - 30 April 1942) |
|||
* Summer-Autumn Campaign ({{lang-ru|Летне-осенняя кампания 1942 г.}}) (1 May - 18 November 1942) |
|||
2. '''[[Second period of World War II]]''' ({{lang-ru|Второй период Великой Отечественной войны}}) (19 November 1942 - 31 December 1943)<br /> |
|||
* Winter Campaign of 1942-43 ({{lang-ru|Зимняя кампания 1942-1943 гг.}}) (19 November 1942 - 3 March 1943) |
|||
* Summer-Autumn Campaign of 1943 ({{lang-ru|Летне-осенняя кампания 1943 г.}}) (1 July - 31 December 1943) |
|||
3. '''[[Third period of World War II]]''' ({{lang-ru|Третий период Великой Отечественной войны}}) (1 January 1944 - 9 May 1945)<br /> |
|||
* Winter-Spring Campaign ({{lang-ru|Зимне-весенняя кампания 1944 г.}}) (1 January - 31 May 1944) |
|||
* Summer-Autumn Campaign of 1944 ({{lang-ru|Летне-осенняя кампания 1944 г.}}) (1 June - 31 December 1944) |
|||
* Campaign in Europe during 1945 ({{lang-ru|Кампания в Европе 1945 г.}}) (1 January - 9 May 1945) |
|||
Excellent analytical works in English written on the history of the combat operation on the Eastern front in the past 20 years include those by [[David Glantz]], which deal with large strategic as well as smaller scale [[Operational warfare|operational]] and [[Engagement (military)|tactical]] aspects of the conflict. |
|||
===Operation Barbarossa: Summer 1941=== |
|||
[[Image:Eastern Front 1941-06 to 1941-12.png|thumb|300px|Operation Barbarossa: the German invasion of the [[Soviet Union]], [[21 June]] [[1941]] to [[5 December]] [[1941]]: |
|||
{{legend|#fff8d5|to 9 July 1941}} |
|||
{{legend|#ffd2b9|to 1 September 1941}} |
|||
{{legend|#ebd7ff|to 9 September 1941}} |
|||
{{legend|#ccffcd|to 5 December 1941}}]] |
|||
[[Operation Barbarossa]] began just before dawn on June 22, 1941. The Germans wrecked the wire network in all Soviet western [[military district]]s to undermine Soviet communications.<ref name="ZHU">{{cite book | last =Zhukov | first =Georgy | authorlink = | coauthors = | title =Vospominaniya i razmyshleniya| publisher =Agenstvo pechati Novosti | year = 1972| location = Moscow| pages = | url = | doi = | id = | isbn = }}</ref> At 03:15 on [[22 June]] [[1941]] ninety-nine (including fourteen [[panzer division]]s and ten motorized) of 190 German divisions, deployed against the Soviet Union began the offensive from the Baltic to the Black seas. They were accompanied by ten Romanian divisions, nine Romanian and four Hungarian [[brigade]]s.<ref>{{cite book | last =Zhilin | first =P.A. (ed.) | authorlink = | coauthors = | title =Velikaya Otechestvennaya voyna| publisher =Izdatelstvo politicheskoi literatury| year = 1973| location = Moscow| pages = | url = | doi = | id = | isbn = }}</ref> On the same day the [[Baltic Military District|Baltic]], [[Western Front (Soviet Union)|Western]] and [[Southwestern Front (Soviet Union)|Kiev Special military districts]] were renamed to [[Northwestern Front|Northwestern]], [[Western Front (Soviet Union)|Western]] and Southwestern Fronts respectively.<ref name="ZHU"/> For a month the offensive conducted on three axes was completely unstoppable as the [[panzer]] forces [[Encirclement|encircled]] hundreds of thousands of Soviet troops in huge pockets that were then reduced by slower-moving [[infantry]] armies while the panzers continued the offensive, following the ''[[Blitzkrieg]]'' [[Military doctrine|doctrine]]. As part of this high tempo campaign the German [[Luftwaffe|air force]] began immediate attacks on Soviet airfields, destroying much of the forward-deployed Soviet Air Force airfield fleets consisting of largely obsolescent types before their pilots had a chance to leave the ground. |
|||
[[Army Group North]]'s objective was [[Saint Petersburg|Leningrad]] via the [[Baltic States]]. Comprising the [[16th Army (Germany)|16th]] and [[18th Army (Germany)|18th armies]] and the [[4th Panzer Army (Germany)|4th Panzer Group]], this formation advanced through [[Lithuania]], [[Latvia]], [[Estonia]], and the Russian [[Pskov Oblast|Pskov]] and [[Novgorod Oblast|Novgorod]] [[oblast]]s. |
|||
[[Army Group Centre]] comprised two panzer groups ([[2nd Panzer Group (Germany)|2nd]] and [[3rd Panzer Group (Germany)|3rd]]), which advanced to the north and south of [[Brest-Litovsk]] and converged east of [[Minsk]], followed by the [[2nd Army (Germany)|2nd]], [[4th Army (Germany)|4th]], and [[9th Army (Germany)|9th armies]]. The combined panzer force reached the [[Berezina river|Beresina River]] in just six days, 650 km (400 miles) from their start lines. The next objective was to cross the [[Dnieper river]], which was accomplished by [[11 July]]. Following that, their next target was [[Smolensk]], which fell on [[16 July]], but the [[Battle of Smolensk (1941)|engagement in the Smolensk area]] halted the German advance until mid-September, effectively disrupting the ''blitzkrieg''. |
|||
[[Army Group South]], with [[1st Panzer Army (Germany)|1st Panzer Group]], [[6th Army (Germany)|6th]], [[11th Army (Germany)|11th]] and [[17th Army (Germany)|17th armies]], was tasked with advancing through [[Galicia (Central Europe)#Second World War and Distrikt Galizien|Galicia]] and into [[Ukraine]]. Their progress, however, was rather slow, and took heavy casualties in a major tank [[Battle of Brody (1941)|battle]]. With the corridor towards [[Kiev]] secured by mid-July, the 11th Army, aided by two Romanian armies, fought its way through [[Bessarabia]] towards [[Odessa]]. The 1st Panzer Group turned away from Kiev for the moment, advancing into the Dnieper bend (western [[Dnipropetrovsk Oblast]]). When it joined up with the southern elements of Army Group South at [[Uman, Ukraine|Uman]], the Group [[Battle of Uman|captured about 100,000 Soviet prisoners]] in a huge encirclement. |
|||
[[Image:Agitplakat.jpg|thumb|200px|Soviet poster of 1941. The inscription reads: "Join the ranks of the front female helpmates, a companion is an aid and friend for fighter!".]] |
|||
As the [[Red Army]] withdrew behind the Dnieper and [[Daugava|Dvina]] rivers, the Soviet [[Stavka]] turned its attention to evacuating as much of the western regions' industry as it could, dismantled and packed onto flatcars, away from the [[front line]], re-establishing it in more remote areas of the [[Ural Mountains|Urals]], [[Caucasus]], [[Central Asia]] and south-eastern [[Siberia]]. Most civilians were left to make their own way East as only the industry-related workers could be evacuated with the equipment, and much of the population was left behind to the mercy of the invading forces. |
|||
With the capture of Smolensk, and the advance to the [[Luga river]], Army groups Centre and North had completed their first major objective: to get across, and hold the "land bridge" between the Dvina and Dnieper. The advance to [[Moscow]], now only 400 km (250 miles) away, could now begin. |
|||
The German generals argued for an immediate offensive towards Moscow, but Hitler [[Lötzen decision|overruled them]], citing the importance of Ukrainian agricultural and mining resources, and heavy industry if under German possession, not to mention the massing of Soviet reserves in the [[Gomel]] area between Army Group Centre's southern flank and the bogged-down Army Group South's northern flank. The order was issued to 2nd Panzer Group to turn south and advance towards Kiev. This took the whole of August and into September, but when 2nd Panzer Group joined up with 1st Panzer Group at [[Lokhvytsia|Lokhvitsa]] on [[14 September]] 665,000 [[Nazi crimes against Soviet POWs|Soviet prisoners]] were captured as [[Battle of Kiev (1941)|Kiev was surrendered]] on [[19 September]]. |
|||
Immediately after the start of the German invasion, the [[NKVD prisoner massacres|NKVD massacred]] large numbers of prisoners in most of their prisons in [[Western Belarus]] and [[Western Ukraine]], while the remainder was to be evacuated in [[death march]]es.<ref>Robert Gellately. ''Lenin, Stalin, and Hitler: The Age of Social Catastrophe.'' [[Knopf]], 2007 ISBN 1400040051 p. 391</ref> Most of them were [[political prisoner]]s, imprisoned and executed without a trial.<ref>{{pl icon}} [[Encyklopedia PWN]], ''[http://encyklopedia.pwn.pl/83293_1.html Zbrodnie Sowickie W Polsce]''</ref> |
|||
===Moscow and Rostov: Autumn 1941=== |
|||
{{Main|Battle of Moscow|Battle of Rostov (1941)}} |
|||
[[Image:Lamenting the dead.jpg|thumb|left|200px|Lamenting the dead. German massacre at [[Kerch]], the [[Crimea]].]] |
|||
Hitler then decided to resume the advance to Moscow, re-designating the panzer groups as panzer armies for the occasion. [[Battle of Moscow|Operation Typhoon]], which was set in motion on [[30 September]], saw 2nd Panzer Army rush along the paved road from [[Orel]] (captured [[5 October]]) to the [[Oka river]] at [[Plavskoye]], while the 4th Panzer Army (transferred from Army Group North to Centre) and 3rd Panzer armies surrounded the Soviet forces in two huge pockets at [[Vyazma]] and [[Bryansk]]. Army Group North positioned itself in front of [[Saint Petersburg|Leningrad]] and attempted to cut the rail link at [[Tikhvin]] to the east. Thus began the 900-day [[Siege of Leningrad]]. North of the [[Arctic Circle]], a German-Finnish force [[Operation Silver Fox|set out for Murmansk]] but could get no further than the [[Zapadnaya Litsa River]], where they settled down. |
|||
Army Group South pushed down from the Dnieper to the [[Sea of Azov]] coast, also advancing through [[Kharkov]], [[Kursk]], and [[Stalino]]. The 11th Army moved into the [[Crimea]] and had taken control of all of the [[peninsula]] by autumn (except [[Sevastopol]], which [[Battle of Sevastopol|held out]] until [[3 July]] [[1942]]). On [[21 November]] the Germans [[Battle of Rostov (1941)|took Rostov]], the gateway to the [[Caucasus]]. However, the German lines were over-extended and the Soviet defenders counterattacked the 1st Panzer Army's spearhead from the north, forcing them to pull out of the city and behind the [[Mius River]]; the first significant German [[Withdrawal (military)|withdrawal]] of the war. |
|||
[[Image:Odessa Soviet artilery.JPG|right|thumb|200px|Soviet gun crew in action at Odessa in 1941]] |
|||
One last lunge on [[15 November]] saw the Germans attempting to throw a ring around Moscow. On [[27 November]] the 4th Panzer Army got within 30 km (19 miles) of the [[Moscow Kremlin|Kremlin]] when it reached the last tramstop of the Moscow line at [[Khimki]], while the 2nd Panzer Army, despite its best efforts, failed to take [[Tula, Russia|Tula]], the last Soviet city that stood in its way of the capital. After a meeting held in [[Orsha]] between the head of the [[Oberkommando des Heeres|Army General Staff]], [[General]] [[Franz Halder|Halder]], and the heads of three [[Army Group|Army]] groups and armies, it was decided to push forward to [[Moscow]] since it was better, as argued by head of [[Army Group Center]], [[Field Marshal]] [[Fedor von Bock]], for them to try their luck on the battlefield rather than just sit and wait while their opponent gathered more strength. |
|||
However, by [[6 December]] it became clear that the ''[[Wehrmacht]]'' was too weak to capture Moscow and the attack was put on hold. [[Marshal]] [[Shaposhnikov]] thus began his [[counter-attack]], employing freshly mobilized [[Military reserve force|reserves]]<ref>Louis Rotundo. The Creation of Soviet Reserves and the 1941 Campaign. Military Affairs, Vol. 50, No. 1 (Jan., 1986), pp. 21-28. </ref>, as well as some well-trained Far-Eastern divisions transferred from the east following the guarantee of [[Richard Sorge|neutrality from Japan]]. |
|||
===Soviet counter-offensive: Winter 1941=== |
|||
[[Image:Eastern Front 1941-12 to 1942-05.png|thumb|300px|The Soviet winter counter-offensive, [[5 December]] [[1941]] to [[7 May]] [[1942]]:{{legend|#ffd2b9|Soviet gains}} |
|||
{{legend|#ccffcd|German gains}}]] |
|||
{{Main|Battle of Moscow|Second Battle of Kharkov}} |
|||
[[Image:EasternFrontMedal.jpg|110px|left|thumb|Over 3 million German and axis personnel were awarded the Winter war in the East 1941/42 (Winterschlacht im Osten 1941/42) medal for service during [[15 November]] [[1941]] - [[15 April]] [[1942]] from its creation on [[26 May]] [[1942]] until [[4 September]] [[1944]]]] |
|||
During the autumn, [[Stalin]] had been transferring fresh and well-equipped Soviet forces from Siberia and the far east to Moscow (these troops had been stationed there in expectation of a Japanese attack, but Stalin's master [[spy]] [[Richard Sorge]] indicated that the Japanese had decided to attack [[South-East Asian Theatre of World War II|Southeast Asia]] and [[Pacific War|the Pacific]] instead). On [[5 December]] [[1941]], these reinforcements attacked the German lines around Moscow, supported by new [[T-34 tank]]s and [[Katyusha rocket launcher]]s. The new Soviet troops were prepared for winter warfare, and they included several [[Ski warfare|ski battalions]]. The exhausted and freezing Germans were routed and driven back between 100 and 250 km (60 to 150 miles) by [[7 January]] [[1942]]. |
|||
A further Soviet attack was mounted in late January, focusing on the junction between Army groups North and Centre between [[Lake Seliger]] and [[Rzhev]], and drove a gap between the two German army groups. In concert with the advance from [[Kaluga]] to the south-west of Moscow, it was intended that the two offensives converge on Smolensk, but the Germans rallied and managed to hold them apart, retaining a [[salient]] at Rzhev. A Soviet [[paratrooper|parachute drop]] on German-held [[Dorogobuzh]] was spectacularly unsuccessful, and those paratroopers who survived had to escape to the partisan-held areas beginning to swell behind German lines. To the north, the Soviets surrounded a German [[garrison]] in [[Demyansk]], which held out with air supply for four months, and established themselves in front of [[Kholm]], [[Velizh]], and [[Velikie Luki]]. |
|||
In the south the Red Army crashed over the [[Donets River]] at [[Izyum]] and drove a 100-km (60-mile) deep salient. The intent was to pin Army Group South against the [[Sea of Azov]], but as the winter eased the Germans were able to counter-attack and cut off the over-extended Soviet troops in the [[Second Battle of Kharkov]]. |
|||
===Don, Volga, and Caucasus: Summer 1942=== |
|||
[[Image:Eastern Front 1942-05 to 1942-11.png|thumb|300px|[[Operation Blue]]: German advances from [[7 May]] [[1942]] to [[18 November]] [[1942]]: |
|||
{{legend|#fff8d5|to 7 July 1942}} |
|||
{{legend|#ffd2b9|to 22 July 1942}} |
|||
{{legend|#ebd7ff|to 1 August 1942}} |
|||
{{legend|#ccffcd|to 18 November 1942}}]] |
|||
{{Main|Battle of Voronezh (1942)|Battle of the Caucasus|Battle of Stalingrad}} |
|||
Although plans were made to attack Moscow again, on [[28 June]] [[1942]], the offensive re-opened in a different direction. Army Group South took the initiative, anchoring the front with the [[Battle of Voronezh (1942)|Battle of Voronezh]] and then following the [[Don River, Russia|Don river]] southeastwards. The grand plan was to secure the Don and [[Volga]] first and then drive into the Caucasus towards the [[oilfield]]s, but operational considerations and Hitler's vanity made him order both objectives to be attempted simultaneously. Rostov was recaptured on [[24 July]] when 1st Panzer Army joined in, and then that group drove south towards [[Maykop|Maikop]]. As part of this, [[Operation Shamil]] was executed, a plan whereby a group of [[Brandenburger commando]]s dressed up as Soviet [[NKVD]] troops to destabilise Maikop's defenses and allow the 1st Panzer Army to enter the oil town with little opposition. |
|||
Meanwhile, 6th Army was driving towards [[Stalingrad]], for a long period unsupported by 4th Panzer Army, which had been diverted to help 1st Panzer Army cross the Don. By the time 4th Panzer Army had rejoined the Stalingrad offensive, Soviet resistance (comprising the 62nd Army under [[Vasily Chuikov]]) had stiffened. A leap across the Don brought German troops to the Volga on [[23 August]] but for the next three months the ''[[Wehrmacht]]'' would be fighting the [[Battle of Stalingrad]] street-by-street. |
|||
Towards the south 1st Panzer Army had reached the Caucasian foothills and the [[Malka River]]. At the end of August Romanian mountain troops joined the Caucasian spearhead, while the Romanian 3rd and 4th armies were redeployed from their successful task of clearing the Azov [[littoral]]. They took up position on either side of Stalingrad to free German troops for the proper fighting. Mindful of the continuing antagonism between Axis allies Romania and [[Hungary]] over [[Transylvania]], the Romanian army in the Don bend was separated from the Hungarian 2nd army by the Italian 8th Army. Thus all of Hitler's allies were involved — including a [[Slovakia]]n contingent with 1st Panzer Army and a [[Croatia]]n [[regiment]] attached to 6th Army. |
|||
The advance into the Caucasus bogged down, with the Germans unable to fight their way past [[Malgobek]] and to the main prize of [[Grozny]]. Instead they switched the direction of their advance to approach it from the south, crossing the Malka at the end of October and entering North [[Ossetia]]. In the first week of November, on the outskirts of [[Ordzhonikidze]], the 13th Panzer Division's spearhead was snipped off and the panzer troops had to fall back. The offensive into Russia was over. |
|||
===Stalingrad: Winter 1942=== |
|||
[[Image:Eastern Front 1942-11 to 1943-03.png|thumb|300px|Operations [[Operation Uranus|Uranus]], [[Operation Saturn|Saturn]] and [[Operation Mars|Mars]]: Soviet advances on the Eastern Front, [[18 November]] [[1942]] to March 1943: |
|||
{{legend|#fff8d5|to 12 December 1942}} |
|||
{{legend|#ffd2b9|to 18 February 1943}} |
|||
{{legend|#ccffcd|to March 1943 (Soviet gains only)}}]] |
|||
{{Main|Battle of Stalingrad|Operation Saturn|Second Rzhev-Sychevka offensive|Third Battle of Kharkov|Battle of Velikiye Luki}} |
|||
While the German 6th Army and 4th Panzer Army had been fighting their way into Stalingrad, Soviet armies had congregated on either side of the city, specifically into the Don [[bridgehead]]s that the Romanians had been unable to reduce, and it was from these that they struck on [[19 November]] [[1942]]. In [[Operation Uranus]], two Soviet fronts punched through the Romanians and converged at [[Kalach]] on [[23 November]], trapping 300,000 Axis troops behind them. A simultaneous offensive on the Rzhev sector known as [[Operation Mars]] was supposed to advance to Smolensk, but was a failure, with German tactical flair winning the day. |
|||
The Germans rushed to transfer troops to Russia for a desperate attempt to relieve Stalingrad, but the offensive could not get going until [[12 December]], by which time the 6th Army in Stalingrad was starving and too weak to break out towards it. [[Operation Wintergewitter|Operation Winter Storm]], with three transferred panzer divisions, got going briskly from [[Kotelnikovo]] towards the [[Aksai river]] but became bogged down 65 km (40 miles) short of its goal. To divert the rescue attempt the Soviets decided to smash the Italians and come down behind the relief attempt if they could, that operation starting on [[16 December]]. What it did accomplish was to destroy many of the aircraft that had been transporting relief supplies to Stalingrad. The fairly limited scope of the Soviet offensive, although still eventually targeted on Rostov, also allowed Hitler time to see sense and pull Army Group A out of the Caucasus and back over the Don. |
|||
On [[31 January]] [[1943]], the 90,000 survivors of the 300,000-man 6th Army surrendered. By that time the Hungarian 2nd Army had also been wiped out. The Soviets advanced from the Don 500 km (300 miles) to the west of Stalingrad, marching through [[Kursk]] (retaken on [[8 February]] [[1943]]) and [[Kharkov]] (retaken [[16 February]] [[1943]]). In order to save the position in the south, the Germans decided to abandon the Rzhev salient in February, freeing enough troops to make a successful [[riposte]] in eastern Ukraine. [[Manstein]]'s counteroffensive, strengthened by a specially trained SS panzer corps equipped with [[Tiger tank]]s, opened on [[20 February]] [[1943]], and fought its way from [[Poltava]] [[Third Battle of Kharkov|back into Kharkov]] in the third week of March, upon which the spring thaw intervened. This had left a glaring bulge in the front centered on Kursk. |
|||
===Kursk: Summer 1943=== |
|||
[[Image:Eastern Front 1943-02 to 1943-08.png|thumb|300px|German advances at [[Third Battle of Kharkov|Kharkov]] and [[Battle of Kursk|Kursk]], [[19 February]] [[1943]] to [[1 August]] [[1943]]: |
|||
{{legend|#ffd2b9|to 18 March 1943}} |
|||
{{legend|#ccffcd|to 1 August 1943}}]] |
|||
{{Main article|Battle of Kursk}} |
|||
After the failure of the attempt to capture Stalingrad, Hitler had deferred planning authority for the upcoming campaign season to the [[German Army High Command]] and reinstated [[Guderian]] to a prominent role, this time as Inspector of Panzer Troops. Debate among the General Staff was polarised, with even Hitler nervous about any attempt to pinch off the Kursk salient. He knew that in the intervening six months the Soviet position at Kursk had been reinforced heavily with [[anti-tank]] guns, [[tank trap]]s, [[land mine|landmines]], [[barbed wire]], [[trench warfare|trenches]], [[pillbox]]es, [[artillery]] and [[Mortar (weapon)|mortars]]. However, if one last great ''[[blitzkrieg]]'' offensive could be mounted, just maybe the Soviets would ease off and attention could then be turned to the Allied threat to the [[Western Front (World War II)|Western Front]]. The advance would be executed from the Orel salient to the north of Kursk and from [[Belgorod]] to the south. Both wings would converge on the area east of [[Kursk]], and by that means restore the lines of [[Army Group South]] to the exact points that it held over the winter of 1941–1942. |
|||
Although the Germans knew that the Red Army's reserves of manpower had been bled dry in the summer of 1941 and 1942, the Soviets were still re-equipping, simply by drafting the men from the regions liberated. |
|||
[[Image:Kursk Soviet Artilery.JPG|thumb|left|200px|Soviet 76.2 mm field guns.]] |
|||
Under pressure from his generals, Hitler bit the bullet and agreed to the attack on Kursk, little realising that the ''[[Abwehr]]'''s intelligence on the Soviet position there had been undermined by a concerted ''[[Stavka]]'' misinformation and [[counter-intelligence]] campaign mounted by the [[Lucy spy ring]] in [[Switzerland]]. When the Germans began the operation, it was after months of delays waiting for new tanks and equipment, by which time the Soviets had reinforced the Kursk salient with more anti-tank firepower than had ever been assembled in one place before or since. |
|||
In the north, the entire [[9th Army]] had been redeployed from the Rzhev salient into the Orel salient and was to advance from Maloarkhangelsk to Kursk. But its forces could not even get past the first objective at [[Olkhovatka]], just 8 km (5 miles) into the advance. The 9th Army blunted its spearhead against the Soviet [[land mine|minefields]], frustratingly so considering that the high ground there was the only natural barrier between them and flat tank country all the way to Kursk. The direction of advance was then switched to [[Ponyri]], to the west of Olkhovatka, but the 9th Army could not break through here either and went over to the defensive. The Soviets simply soaked up the German punishment and then struck back. On [[12 July]] the Red Army battled through the demarcation line between the 211th and 293rd divisions on the [[Zhizdra River]] and steamed towards [[Karachev]], right behind them and behind Orel. |
|||
<!-- Image with inadequate rationale removed: [[Image:Totenkopf-Kursk-01.jpg|thumb|200px|Waffen-SS ''[[Panzergrenadier]]s'' of the 3rd SS-Panzer-Division ''[[SS Division Totenkopf|Totenkopf]]'' and Wehrmacht Tiger tanks at the start of the [[Battle of Kursk]].]] --> |
|||
The southern offensive, spearheaded by [[German 4th Panzer Army|4.Panzer-Armee]], led by [[Hermann Hoth|Gen. Col. Hoth]], with three Tank Corps made more headway. Advancing on either side of the upper Donets on a narrow corridor, the [[II SS Panzer Corps|SS Panzer Corps]] and the [[Grossdeutschland Division|Großdeutschland Panzergrenadier divisions]] battled their way through minefields and over comparatively high ground towards [[Oboyan]]. Stiff resistance caused a change of direction from east to west of the front, but the tanks got 25 km (15 miles) before encountering the reserves of the [[Soviet 5th Guards Tank Army]] outside [[Prokhorovka]]. Battle was joined on [[12 July]], with about one thousand tanks doing battle. After the war, the battle near Prochorovka was idealized by the Soviet [[historian]]s as the biggest tank battle of all time. The meeting engagement at Prochorovka was a Soviet defensive success, albeit at heavy cost. The Soviet 5th Guards Tank Army, with about 800 light and medium tanks, attacked elements of the II SS Panzer Corps. Tank losses on both sides have been the source of controversy ever since. Although the 5th Guards Tank Army did not attain their terrain objectives, the German advance was halted. |
|||
[[Image:Kursk captured German tank.JPG|thumb|right|200px|Marshal Zhukov and Colonel General Nikolai Voronov, commander of Red Army Artillery, (front row left to right) inspect a German Tiger tank captured near Leningrad.]] |
|||
At the end of the day both sides had fought each other to a standstill, but regardless of the standstill in the north [[Manstein]] intended to continue the attack with the 4th Panzer Army. But the Soviets could absorb the attack, and German strategic advance in [[Operation Citadel]] had been halted. Under the impression of the successful [[counter-attack]] operations in the south the Red Army started the strong offensive operation in the northern Orel salient and achieved a breakthrough on the flank of the German 9th Army. Also worried by the Allies' [[Operation Husky|landing in Sicily]] on [[10 July]], Hitler made the decision to halve the offensive even as the German 9th Army was rapidly giving ground in the north. The Germans' final strategic offensive in the Soviet Union ended with their defense against a major Soviet counteroffensive that lasted into August. A detailed analysis of this campaign is available in the [[Battle of Kursk|Battle of Kursk article]]. |
|||
The Kursk offensive was the last on the scale of 1940 and 1941 the ''Wehrmacht'' was able to launch, and subsequent offensives would represent only a shadow of previous German offensive might. Following the defeat, Hitler would not trust his generals to the same extent again, and the quality of German strategic decision fell correspondingly. The Battle of Kursk cost Hitler over 500,000 troops and 1,000 tanks, forever hampering future war efforts on the Eastern Front. |
|||
===Autumn and Winter 1943=== |
|||
{{Main|Korsun-Cherkassy Pocket|Battle of Smolensk (1943)|Battle of the Lower Dnieper|Battle of Narva (1944)}} |
|||
The Soviet juggernaut got rolling in earnest with the advance into the Germans' Orel salient. The diversion of Hitler's favourite ''[[Grossdeutschland Division]]'' from Belgorod to Karachev could not stop it, and a strategic decision was made to abandon Orel (retaken by the Red Army on [[5 August]] [[1943]]) and fall back to the Hagen line in front of [[Bryansk]]. To the south, the Soviets blasted through Army Group South's Belgorod positions and headed for Kharkov once again. Though intense battles of movement throughout late July and into August 1943 saw the [[Tiger I|Tiger]]s blunting Soviet tanks on one axis, they were soon outflanked on another line to the west as the Soviets advanced down the [[Psel]], and Kharkov had to be evacuated for the final time on [[22 August]]. |
|||
[[Image:German pow 1943 by Soviet troops.JPG|left|250px|thumb|German prisoners being searched by Red Army soldiers]] |
|||
The German forces on the [[Mius]], now constituting the 1st Panzer Army and a reconstituted 6th Army, were by August too weak to sustain a Soviet attack on their own front, and when the Soviets hit them they had to fall back all the way through the [[Donbass]] industrial region to the Dnieper, losing the industrial resources and half the farmland that Germany had invaded the Soviet Union to exploit. At this time Hitler agreed to a general withdrawal to the Dnieper line, along which was meant to be the ''Ostwall'', a line of defence similar to the [[Westwall#Reactivation of the Siegfried Line, 1944|Westwall]] of fortifications along the German frontier in the west. Trouble was, it hadn't been built yet, and by the time Army Group South had evacuated eastern Ukraine and begun withdrawing across the Dnieper during September, the Soviets were hard behind them. Tenaciously, small units paddled their way across the 3-km (2-mile) wide river and established [[bridgehead]]s. A second attempt by the Soviets to gain land using parachutists, mounted at [[Kanev]] on [[24 September]], proved as luckless as at Dorogobuzh eighteen months previously, and the paratroopers were soon repelled — but not before still more Red Army troops had used the cover they provided to get themselves over the Dnieper and securely dug in. As September proceeded into October, the Germans found the Dnieper line impossible to hold as the Soviet bridgeheads grew and grew, and important Dnieper towns started to fall, with [[Zaporozhye]] the first to go, followed by [[Dnepropetrovsk]]. Finally, early in November the Soviets broke out of their bridgeheads on either side of Kiev and captured the Ukrainian capital, at that time the third largest city in the Soviet Union. |
|||
Eighty miles west of Kiev, the 4th Panzer Army, still convinced that the Red Army was a spent force, was able to mount a successful riposte at [[Zhitomir]] during the middle of November, blunting the Soviet bridgehead via a daring outflanking strike mounted by the SS Panzer Corps along the river Teterev. This battle also enabled Army Group South to recapture Korosten and gain some time to rest; however, on [[Christmas Eve]] the retreat began anew when the First Ukrainian Front (renamed from Voronezh Front) struck them in the same place. The Soviet advance continued along the railway line until the 1939 Polish-Soviet border was reached on 3 January 1944. To the south, Second Ukrainian Front (ex [[Steppe Front]]) had crossed the Dnieper at [[Kremenchug]] and continued westwards. In the second week of January 1944 they swung north, meeting Vatutin's tank forces who had swung south from their penetration into Poland and surrounding ten German divisions at Korsun-Shevenkovsky, west of [[Korsun Pocket|Cherkassy]]. Hitler's insistence on holding the Dnieper line, even when facing the prospect of catastrophic defeat, was compounded by his conviction that the Cherkassy pocket could break out and even advance to Kiev, but Manstein was more concerned about being able to advance to the edge of the pocket and then implore the surrounded forces to break out. By 16 February the first stage was complete, with panzers separated from the contracting Cherkassy pocket only by the swollen Gniloy Tikich river. Under shellfire and pursued by Soviet tanks, the surrounded German troops, among whom were the [[SS Division (motorised) Wiking|SS Division Wiking]], fought their way across the river to safety, losing half their number and all their equipment. Surely the Soviets would not attack again, with the spring approaching - but in March 3 the Soviet ''Ukrainian Front'' went over to the offensive. Having already isolated the Crimea by severing the neck of the [[Isthmus of Perekop|Perekop isthmus]], Malinovsky's forces advanced across the mud to the [[Romania]]n border, not stopping on the river [[Prut]]. |
|||
[[Image:Eastern Front 1943-08 to 1944-12.png|thumb|300px|Soviet advances from [[1 August]] [[1943]] to [[31 December]] [[1944]]: |
|||
{{legend|#fff8d5|to 1 December 1943}} |
|||
{{legend|#ffd2b9|to 30 April 1944}} |
|||
{{legend|#ebd7ff|to 19 August 1944}} |
|||
{{legend|#ccffcd|to 31 December 1944}}]] |
|||
One final move in the south completed the 1943-44 campaigning season, which had wrapped up an advance of over 500 miles. In March, 20 German divisions of ''[[Generaloberst]]'' [[Hans-Valentin Hube]]'s [[German First Panzer Army|1st Panzer Army]] were encircled in what was to be known as [[Hube's Pocket]] near Kamenets-Podolskiy. After two weeks hard fighting, the 1st Panzer managed to escape the pocket, suffering only light to moderate casualties. At this point, Hitler sacked several prominent generals, Manstein included. April saw the liberation of [[Odessa]] in April 1944, followed by 4th Ukrainian Front's campaign to liberate the Crimea, which culminated with the liberation of [[Sevastopol]] on 10 May. |
|||
Along Army Group Centre's front, August 1943 saw this force pushed back from the Hagen line slowly, ceding comparatively little territory, but the loss of Bryansk and more importantly, Smolensk, on [[25 September]] cost the Wehrmacht the keystone of the entire German defensive system. The 4th and 9th armies and 3rd Panzer Army still held their own east of the upper Dnieper, stifling Soviet attempts to reach Vitebsk. On Army Group North's front, there was barely any fighting at all until January 1944, when out of nowhere Volkhov and Second Baltic Fronts struck. In a lightning campaign, Leningrad and [[Novgorod]] were liberated. By February the Red Army had reached the borders of [[Estonia]] after a 75 mile advance. The Baltic Sea seemed the quickest way to Stalin to take the battles to the German ground in [[East Prussia]] and seizing control of Finland.<ref name=glantz>{{cite book|author=David M. Glantz|title=The Battle for Leningrad: 1941-1944|publisher=University Press of Kansas|location=Lawrence|year=2002}}</ref> The Soviet [[Battle for Narva Bridgehead|offensive towards the Baltic port of Tallinn was stopped]] in February 1944. The German forces included [[Occupation of Estonia by Nazi Germany#Estonians in German Military Units in 1941-1944|Estonian conscripts and volunteers]], defending the [[Estonian Government in Exile#Failure to reestablish independence|re-establishment of Estonian independence]].<ref>[http://books.google.com/books?ei=cm01R5fMF5SysgP38dmFAg&id=V4siAAAAMAAJ&dq=%22Otto+Tief+%22&q=Otto+Tief&pgis=1#search Estonia. Sept.21] Bulletin of International News by Royal Institute of International Affairs Information Dept.</ref><ref name=vm>{{cite web|url=http://web-test.vm.ee/estonia/pea_172/kat_509/7786.html|publisher=Estonian Ministry of Foreign Affairs|title=The Otto Tief government and the fall of Tallinn|year=2006}}</ref> |
|||
===Summer 1944=== |
|||
{{Main|Battle of the Crimea (1944)|Belorussian Offensive|Lvov-Sandomir Offensive|Battle of Tannenberg Line|Warsaw Uprising|Slovak National Uprising|Battle of Romania (1944)|Battle of Debrecen|}} |
|||
''Wehrmacht'' planning was convinced that the Soviets would attack again in the south, where the front was fifty miles from [[Lvov]] and offered the most direct route to [[Berlin]]. Accordingly they stripped troops from Army Group Centre, whose front still protruded deep into the Soviet Union. The Belorussian Offensive (codenamed [[Operation Bagration]]) started on [[June 22]] [[1944]], was a massive Soviet attack, consisting of four Soviet army groups totaling over 120 divisions that smashed into a thinly-held German line. They focused their massive attacks on Army Group Centre, not Army Group South as the Germans had originally expected. The Germans had transferred some units to France to counter the [[Battle of Normandy|invasion of Normandy]] two weeks before. The Red Army achieved a ratio of ten to one in tanks and seven to one in [[aircraft]] over the enemy. At the points of attack, the numerical and quality advantages of the Soviets were overwhelming. More than 2.3 million Soviet troops went into action against the German Army Group Centre, which could boast a strength of less than 800,000 men. The Germans crumbled. The capital of [[Belarus]], [[Minsk]], was taken on [[July 3]], trapping 50,000 Germans. Ten days later the Red Army reached the prewar [[Poland|Polish]] border. ''Bagration'' was by any measure one of the largest single operations of the war. By the end of August 1944 it had cost the Red Army ~170,000 dead and missing (765,815 totally, including wounded and sick plus 5073 Poles),<ref name=autogenerated3>G. I. Krivosheev. Soviet Casualties and Combat Losses. Greenhill 1997 ISBN 1-85367-280-7</ref> as well as 2,957 tanks and assault guns. In the operations, the Germans lost approximately 670,000 dead, missing, wounded and sick, out of whom 160,000 were captured, as well as 2,000 tanks and 57,000 other vehicles. |
|||
The neighbouring [[Lvov-Sandomir Offensive|Lvov-Sandomierz operation]] was launched on [[17 July]] [[1944]], rapidly routing the German forces in the western Ukraine. The Soviet advance in the south continued into [[Battle of Romania (1944)|Romania]] and, following a coup against the Axis-allied government of Romania on [[August 23]], the Red Army occupied [[Bucharest]] on [[August 31]]. In Moscow on [[September 12]], Romania and the Soviet Union signed an [[armistice]] on terms Moscow virtually dictated. The Romanian surrender tore a hole in the southern German Eastern Front causing the inevitable loss of the whole of the [[Balkans]]. |
|||
The rapid progress of Operation Bagration threatened to cut off and isolate the German units of [[Army Group North]] bitterly [[Battle of Narva (1944)|resisting the Soviet advance]] to the [[Baltic Sea|Baltic]] port of [[Tallinn]] and the [[Estonia in World War II#Soviet return|Soviet re-occupation]] of Estonia. In a ferocious attempt in the [[Sinimäed Hills]], Estonia, the Soviet Leningrad Front [[Battle of Tannenberg Line|failed to break through]] the defence of the smaller well-fortified Army Group Narwa in a [[Battle of Narva (1944)#Terrain|terrain not suitable for large scale operations]].<ref name=white>{{cite book|author=Estonian State Commission on Examination of Policies of Repression|url=http://www.just.ee/orb.aw/class=file/action=preview/id=12709/TheWhiteBook.pdf|format=PDF|publisher=Estonian Encyclopedia Publishers|title=The White Book: Losses inflicted on the Estonian nation by occupation regimes. 1940 – 1991|year=2005}}</ref><ref name=hiio>{{cite book|author=Toomas Hiio|year=1999|title=Combat in Estonia in 1944. In: Toomas Hiio, Meelis Maripuu, Indrek Paavle (Eds.). Estonia 1940–1945: Reports of the Estonian International Commission for the Investigation of Crimes Against Humanity|location=Tallinn}}</ref> |
|||
In Poland, as the Red Army approached, the [[Polish Home Army]] (AK) launched [[Operation Tempest]]. During the [[Warsaw Uprising]], the Soviet Army halted at the [[Vistula River]], unable or unwilling to come to the aid of the Polish resistance. An attempt by the communist controlled [[1st Polish Army]] to relieve the city was unsupported by the Red Army and was thrown back in September with heavy losses. |
|||
In [[Slovakia]], the [[Slovak National Uprising]] started as an armed struggle between German ''Wehrmacht'' forces and rebel Slovak troops in August to October 1944. It was centered at [[Banská Bystrica]]. |
|||
===Autumn 1944=== |
|||
{{Main|Baltic Offensive|Budapest Offensive}} |
|||
On 8 September 1944 the Red Army begun an attack on the [[Dukla Pass]] on the Slovak-Polish border. Two months later, the Soviets won the battle and entered Slovakia. The toll was high: 85,000 Red Army soldiers lay dead, plus several thousand Germans, Slovaks and [[Czechoslovakia|Czechs]]. |
|||
Under the pressure of the Soviet [[Baltic Offensive]], the German Army Group North were withdrawn to fight in the sieges of [[Moonzund Landing Operation|Saaremaa]], [[Courland Pocket|Courland]] and [[Siege of Memel|Memel]]. |
|||
===January-March 1945=== |
|||
[[Image:Eastern Front 1945-01 to 1945-05.png|thumb|300px|Soviet advances from [[1 January]] [[1945]] to [[7 May]] [[1945]]: |
|||
{{legend|#ffd2b9|to 30 March 1945}} |
|||
{{legend|#ccffcd|to 11 May 1945}}]] |
|||
''Main articles: [[Vistula-Oder Offensive]] (January-February) with the follow-up [[East Pomeranian Offensive]] and [[Silesian Offensives]] (February-April), [[East Prussian Offensive]] (January-April), [[Vienna Offensive]] (March-April)'' |
|||
The Soviet Union finally entered [[Warsaw]] in January 1945, after it was destroyed and abandoned by the Germans. Over three days, on a broad front incorporating four army [[Front (Soviet Army)|front]]s, the Red Army began an offensive across the [[Narew]] River and from Warsaw. The Soviets outnumbered the Germans on average by five~six to one in troops, six to one in artillery, six to one in tanks and four to one in [[self-propelled artillery]]. After four days the Red Army broke out and started moving thirty to forty kilometres a day, taking the Baltic states, [[Danzig]], [[East Prussia]], [[Poznań]], and drawing up on a line sixty kilometres east of [[Berlin]] along the [[Oder]] River. During the full course of the Vistula-Oder operation (23 days), the Red Army forces sustained 194,000 total casualties (killed, wounded, and missing) and lost 1,267 tanks and assault guns. |
|||
On [[25 January]] [[1945]], Hitler renamed three army groups. [[Army Group North]] became [[Army Group Courland]]; Army Group Centre became Army Group North and [[Army Group A]] became Army Group Centre. Army Group North (old Army Group Centre) was driven into an ever smaller pocket around [[Kaliningrad#Third Reich|Königsberg]] in [[East Prussia]]. |
|||
A limited counter-attack (codenamed [[Operation Solstice]]) by the newly created [[Army Group Vistula]], under the command of ''[[Reichsführer-SS]]'' [[Heinrich Himmler]], had failed by [[February 24]], and the Soviets drove on to [[Pomerania]] and cleared the right bank of the Oder River. In the south, three German attempts to relieve the encircled [[Budapest]] failed and the city fell on [[February 13]] to the Soviets. Again the Germans counter-attacked, [[Hitler]] insisting on the impossible task of regaining the [[Danube]] River. By [[March 16]] the attack had failed and the Red Army counterattacked the same day. On [[March 30]] they entered [[Austria]] and captured [[Vienna]] on [[April 13]]. |
|||
OKW claim german losses of 377,000 killed, 334, 000 wounded and 292,000 missing, with a total of |
|||
1.103,000 men, on the Eastern Front during January and February 1945. <ref>Hastings, Max, ''Armageddon: The Battle for Germany 1944-1945'', Vintage Books USA</ref> |
|||
[[Image:Soviet pressing 1944.JPG|thumb|right|300px|Soviet tanks and infantry pressing on the Germans near Budapest.]] |
|||
On [[April 9]], [[1945]], [[Königsberg]] finally fell to the Red Army, although the shattered remnants of Army Group North continued to resist on the [[Heiligenbeil]] and [[Danzig]] beachheads until the end of the war in Europe. The East Prussian operation, though often overshadowed by the Vistula-Oder operation and the later battle for Berlin, was in fact one of the largest and costliest operations fought by the Red army through the war. During the period it lasted (13 January - 25 April), it cost the Red Army 584,788 casualties, and 3,525 tanks and assault guns. |
|||
By early April, the [[Stavka]] freed up General [[Konstantin Rokossovsky]]'s [[2nd Belorussian Front]] (2BF) to move west to the east bank of the Oder river. During the first two weeks of April, the Soviets performed their fastest front redeployment of the war. General [[Georgy Zhukov]] concentrated his [[1st Belorussian Front]] (1BF), which had been deployed along the Oder river from [[Frankfurt an der Oder|Frankfurt]] in the south to the Baltic, into an area in front of the [[Seelow Heights]]. The 2BF moved into the positions being vacated by the 1BF north of the Seelow Heights. While this redeployment was in progress gaps were left in the lines and the remnants of the German 2nd Army, which had been bottled up in a pocket near [[Danzig]], managed to escape across the Oder. To the south General [[Ivan Konev]] shifted the main weight of the [[1st Ukrainian Front]] (1UF) out of [[Upper Silesia]] north-west to the [[Neisse]] River.<ref name=Ziemke71>Ziemke, ''Berlin'', see [[#References|References]] page 71</ref> The three Soviet fronts had altogether 2.5 million men (including 78,556 soldiers of the [[1st Polish Army]]); 6,250 tanks; 7,500 aircraft; 41,600 [[artillery]] pieces and [[Mortar (weapon)|mortars]]; 3,255 [[truck]]-mounted [[Katyusha]]s [[rocket]]s, (nicknamed "Stalin Organs"); and 95,383 motor vehicles, many manufactured in the USA.<ref name=Ziemke71/> |
|||
===End of War: April–May 1945=== |
|||
''Main articles: [[Battle of Berlin]], [[Battle of Halbe]], [[Prague Offensive]]'' |
|||
[[Image:Za pobedu nad germanie.jpg|thumb|left|110px|14,933,000 Soviet and Soviet influence nations personnel were awarded the medal for victory over Germany from 9th May 1945.]] |
|||
All that was left for the Soviets to do was to launch an offensive to capture what was to become [[East Germany]]. The Soviet offensive had two objectives. Because of [[Joseph Stalin|Stalin]]'s suspicions about the intentions of the [[Western Allies]] to hand over territory occupied by them in the post-war Soviet [[Sphere of influence|zone of occupation]], the offensive was to be on a broad front and was to move as rapidly as possible to the west, to meet the Western Allies as far west as possible. But the overriding objective was to capture Berlin. The two were complementary because possession of the zone could not be won quickly unless Berlin was taken. Another consideration was that Berlin itself held strategic assets, including Adolf Hitler and the [[German nuclear energy project|German atomic bomb]] program.<ref>Beevor, ''Berlin'', see [[#References|References]] Page 138</ref> [[Image:Ruslanova.jpg|thumb|300px|[[Lidiya Ruslanova]] performing for Soviet soldiers during the Great Patriotic War.]] |
|||
The [[Battle of Berlin|offensive to capture East Germany and Berlin]] started on [[April 16]] with an assault on the [[Battle of Berlin#The battle of Oder-Neisse|German front lines on the Oder and Neisse rivers]]. After several days of heavy fighting the Soviet 1BF and 1UF had punched holes through the German front line and were fanning out across East Germany. By the [[April 24]] elements of the 1BF and 1UF had completed the [[encirclement]] of Berlin and the [[Battle of Berlin]] entered its final stages. On [[April 25]] the 2BF broke through the German 3rd Panzer Army's line south of [[Stettin]]. They were now free to move west towards the [[British 21st Army Group]] and north towards the Baltic port of [[Stralsund]]. The [[58th Guards Rifle Division]] of the [[5th Guards Army]] made contact with the [[US 69th Infantry Division]] of the [[U.S. First Army|First Army]] near [[Torgau]], Germany at the [[Elbe]] river.<ref name=Beevor217-233>Beevor, ''Berlin'', see [[#References|References]] pp. 217-233</ref><ref name=Ziemke81>Ziemke , ''Berlin'', see [[#References|References]] page 81-111</ref> |
|||
On [[April 30]], as the Soviet forces fought their way into the centre of Berlin, Adolf Hitler married [[Eva Braun]] and then [[Hitler's death|committed suicide]] by taking [[cyanide]] and shooting himself. [[Helmuth Weidling]], defence commandant of Berlin, surrendered the city to the Soviets on [[May 2]].<ref name=Beevor-259>Beevor, ''Berlin'', see [[#References|References]] pp. 259-357, 380-381</ref> Altogether, the Berlin operation (16 April - 8 May) cost the Red Army 81,367 casualties (dead, missing, wounded and sick) and 1,997 tanks and assault guns. German losses in this period of the war remain impossible to determine with any reliability.{{Fact|date=July 2007}} |
|||
At 22:41 on the morning of [[May 7]], [[1945]], at the [[SHAEF]] headquarters, German Chief-of-Staff General [[Alfred Jodl]] signed the [[unconditional surrender]] documents for all German forces to the Allies. It included the phrase ''All forces under German control to cease active operations at 2301 hours Central European time on [[May 8]] [[1945]]''. The next day shortly before midnight, Field Marshal [[Wilhelm Keitel]] repeated the signing in Berlin at Zhukov's headquarters. [[The end of World War II in Europe|The war in Europe was over]].<ref>Ziemke, ''occupation'', [[#References|References]] [http://www.globalsecurity.org/military/library/report/other/us-army_germany_1944-46_ch15.htm#b3 CHAPTER XV:The Victory Sealed] Page 258 last paragraph</ref> |
|||
In the Soviet Union the end of the war is considered to be [[May 9]], when the surrender took effect [[Moscow]] time. This date is celebrated as a [[Public holiday|national holiday]] - [[Victory Day (Eastern Europe)|Victory Day]] - in [[Russia]] (as part of a two-day May 8-9 holiday) and some other post-Soviet countries. The [[Moscow Victory Parade of 1945|ceremonial Victory parade]] was held in Moscow on [[June 24]]. |
|||
German [[Army Group Centre]] initially refused to surrender and continued to [[Prague Offensive|fight in Czechoslovakia]] until about [[May 11]].<ref name=Ziemke-134>Ziemke, ''Berlin'', [[#References|References]] p. 134</ref> |
|||
A small German garrison on the island of Bornholm (Denmark) refused to surrender until after being bombed and invaded by the Soviets. The island was returned to the Danish government four months later. |
|||
===[[Russian Far East|Soviet Far East]]: August 1945=== |
|||
{{main|Manchurian Strategic Offensive Operation}} |
|||
The [[Manchurian Strategic Offensive Operation]] began on August 8, 1945, with the Soviet invasion of the Japanese puppet states of [[Manchukuo]] and neighbouring [[Mengjiang]]; the greater offensive would eventually include northern [[Korea]], southern [[Sakhalin]], and the [[Kuril Islands]]. It marked the initial and only military action of the Soviet Union against the [[Empire of Japan]]; at the [[Yalta Conference]], it had agreed to Allied pleas to terminate the neutrality pact with Japan and enter the Second World War's Pacific theatre within three months after the end of the war in Europe. While not a part of the Eastern Front operations, it is included here because the commanders and much of the forces used by the Red Army, came from the European Theatre of operations and benefited from the experience gained there. In many ways this was a 'perfect' operation, delivered with the skill gained during the bitter fighting with the Wehrmacht and Luftwaffe over four years<ref>Raymond L. Garthoff. The Soviet Manchurian Campaign, August 1945. Military Affairs, Vol. 33, No. 2 (Oct., 1969), pp. 312-336</ref>. |
|||
==Leadership== |
|||
The Soviet Union and Nazi Germany were ideologically driven states, in which the leader had near-absolute power. The character of the war was thus determined by the leaders and their ideology to a much greater extent than in any other theatre of World War II. |
|||
===Adolf Hitler=== |
|||
{{main|Adolf Hitler}} |
|||
[[Image:Adolf Hitler cph 3a48970.jpg|thumb|150px|[[Adolf Hitler]] led Germany during World War II.]] |
|||
Adolf Hitler exercised a tight control over the war, spending much of his time in his command bunkers (most notably at [[Rastenburg]] in [[East Prussia]], at [[Vinnitsa]] in [[Ukraine]], and under the garden of the [[Reich Chancellery]] in [[Berlin]]). At crucial periods in the war he held daily situation conferences, at which he used his remarkable talent for public speaking to overwhelm opposition from his generals and the OKW staff with rhetoric. |
|||
In part because of the unexpected success of the [[Battle of France]] despite the warnings of the professional military, Hitler believed himself a military genius, with a grasp of the total war effort that eluded his generals. In August 1941 when [[Walther von Brauchitsch]] (commander-in-chief of the [[Wehrmacht]]) and [[Fedor von Bock]] were appealing for an attack on Moscow, Hitler instead ordered the encirclement and capture of Ukraine, in order to acquire the farmland, industry, and natural resources of that country. Some historians believe that this decision was a missed opportunity to win the war. |
|||
In the winter of 1941–42 Hitler believed that his obstinate refusal to allow the German armies to retreat had saved [[Army Group Centre]] from collapse. He later told [[Erhard Milch]], |
|||
:I had to act ruthlessly. I had to send even my closest generals packing, two army generals, for example … I could only tell these gentlemen, "Get yourself back to Germany as rapidly as you can — but leave the army in my charge. And the army is staying at the front." |
|||
The success of this [[hedgehog defence]] outside Moscow led Hitler to insist on the holding of territory when it made no military sense, and to sack generals who retreated without orders. Officers with initiative were replaced with yes-men or fanatical Nazis. The disastrous encirclements later in the war — at [[Battle of Stalingrad|Stalingrad]], [[Korsun-Cherkassy Pocket|Korsun]] and many other places — were the direct result of Hitler's orders. Many divisions became cut off in "fortress" cities, or wasted uselessly in secondary theatres, because Hitler would not sanction retreat or abandon voluntarily any of his conquests. |
|||
Frustration at Hitler's leadership of the war was one of the factors in the attempted [[coup d'etat]] of 1944, but after the failure of the [[July 20 Plot]] Hitler considered the army and its officer corps suspect and came to rely on the [[Schutzstaffel]] and Nazi party members to prosecute the war. His many disastrous appointments included that of [[Heinrich Himmler]] to command [[Army Group Vistula]] in the defence of Berlin in 1945 — Himmler suffered a mental breakdown under the stress of the command and was quickly replaced by [[Gotthard Heinrici]]. |
|||
Hitler's direction of the war was disastrous for the German Army, though the skill, loyalty, professionalism and endurance of officers and soldiers enabled him to keep Germany fighting to the end. [[F. W. Winterbotham]] wrote of Hitler's signal to [[Gerd von Rundstedt]] to continue the attack to the west during the [[Battle of the Bulge]]: |
|||
:"''From experience we had learned that when Hitler started refusing to do what the generals recommended, things started to go wrong, and this was to be no exception.''" |
|||
===Joseph Stalin=== |
|||
{{main|Joseph Stalin}} |
|||
Joseph Stalin bore the greatest responsibility for the disasters at the beginning of the war, but can be equally praised for the subsequent success of the Soviet Army, which would have been impossible without the unprecedentedly [[History of the Soviet Union (1927-1953)|rapid industrialization of the Soviet Union]], which was the first priority of Stalin's internal policy throughout the 1930s. |
|||
Stalin's [[Great Purge]] of the [[Red Army]] in the late 1930s consisted of the legal prosecution of many of the senior command, many of whom were convicted and sentenced to death or imprisonment. The executed included [[Mikhail Tukhachevsky]], the brilliant proponent of armoured [[blitzkrieg]]. Stalin promoted some [[obscurantist]]s like [[Grigory Kulik]] (who opposed the mechanization of the army and the production of [[tank]]s), but on the other hand the purge of the older commanders who had had their positions since the [[Russian Civil War]], and had experience, but were deemed “politically unreliable”. This opened up those places to the promotion of many younger officers that Stalin and the NKVD thought were in line with Stalinist politics, many of whom proved to be terribly inexperienced, but some were later very successful. Soviet tank output remained the largest in the world. Distrust of the military led, since the foundation of the Red Army in 1918, to a system of "dual command", in which every commander was paired with a [[political commissar]], a member of the [[Communist Party of the Soviet Union]]. Larger units had military councils consisting of the commander, commissar and chief of staff, who ensured that the commanding officer was loyal and implemented Party orders. |
|||
Following the Soviet occupation of eastern [[Poland]], the Baltic states and [[Bessarabia]] in 1939–40, Stalin insisted that every fold of the new territories should be occupied; this move westward left troops far from their depots in salients that left them vulnerable to encirclement. There was an assumption that, in the event of a German invasion, the Red Army would take the strategic offensive and fight the war mostly outside the borders of the Soviet Union; thus few plans were made for strategic defensive operations. However, fortifications were built. As tension heightened in spring 1941, Stalin was desperate not to give Hitler any provocation that could be used as an excuse for an attack; this caused him to refuse to allow the military to go onto the alert even as German troops gathered on the borders and German reconnaissance planes overflew installations. This refusal to take the necessary action was instrumental in the destruction of major portions of the Red Air Force, lined up on its airfields, in the first days of the war. |
|||
Stalin's insistence on repeated counterattacks without adequate preparation led to the loss of almost the whole of the Red Army's tank corps in 1941 — many tanks simply ran out of fuel on their way to the battlefield through faulty planning or ignorance of the location of fuel dumps. While some regard this offensive strategy as an argument for Soviet aggressive strategic plans, the offensive operational planning was not, by itself, evidence of any aggressive foreign policy intent. |
|||
Unlike Hitler, Stalin was able to learn lessons and improve his conduct of the war. He gradually came to realise the dangers of inadequate preparation and built up a competent command and control organization — the [[Stavka]] — under [[Semyon Timoshenko]], [[Georgy Zhukov]] and others. Incompetent commanders were gradually but ruthlessly weeded out. |
|||
At the crisis of the war, in autumn 1942, Stalin made many concessions to the army: unitary command was restored by removing the Commissars from the [[chain of command]]. After the [[Battle of Stalingrad]], shoulderboards were introduced for all ranks; this was a significant symbolic step, since they had been seen as a symbol of the old regime after the [[Russian Revolution of 1917]]. Beginning in autumn 1941, units that had proved themselves by superior performance in combat were given the traditional "Guards" title. But these concessions were combined with ruthless discipline: [[Order No. 227]], issued on [[28 July]] [[1942]], threatened commanders who retreated without orders with punishment by [[court-martial]]. Infractions by military and ''[[politruk]]s'' were punished with transferral to [[penal battalion]]s and penal [[company (military unit)|companies]], and the [[NKVD]]'s [[barrier troops]] would shoot soldiers who fled. |
|||
As it became clear that the Soviet Union would win the war, Stalin ensured that propaganda always mentioned his leadership of the war; the victorious generals were sidelined and never allowed to develop into political rivals. After the war the Red Army was once again purged (but not as brutally as in the 1930s): many successful officers were demoted to unimportant positions (including [[Georgy Zhukov|Zhukov]], [[Rodion Malinovsky|Malinovsky]] and [[Ivan Koniev|Koniev]]). |
|||
==Occupation and repression== |
|||
<!-- Image with inadequate rationale removed: [[Image:Einsatzgruppen Killing.jpg|right|thumb|200px|A member of ''[[Einsatzgruppe]] D'' murders a Jew who is kneeling before a filled mass grave in [[Vinnitsa]], in 1942. The back of the photo is inscribed "The last Jew in Vinnitsa".]] --> |
|||
The enormous territorial gains of 1941 presented Germany with vast areas to [[pacify]] and administer. Some Soviet citizens, especially in the recently occupied territories of Western Ukraine and the Baltic States greeted their conquerors as liberators from the Soviet rule. However, nascent national liberation movements among [[Ukrainians]] and [[Cossack]]s, and others were viewed by Hitler with suspicion; some, (especially those from the Baltic States) were co-opted into the Axis armies and others brutally suppressed. None of the conquered territories gained any measure of self-rule. Instead, the [[racism|racist]] [[Nazism|Nazi ideologues]] saw the future of the East as one of [[Generalplan Ost|settlement by German colonists]], with the natives killed, expelled, or reduced to slave labour ([[Generalplan Ost]]). |
|||
Regions closer to the front were managed by military powers of the region, in other areas such as Baltic states annexed by USSR in 1940, Reichscommissariats were established. As a rule, the maximum in loot was extracted. In September 1941, [[Erich Koch]] was appointed to the Ukrainian Commissariat. His opening speech was clear about German policy: "I am known as a brutal dog … Our job is to suck from Ukraine all the goods we can get hold of ... I am expecting from you the utmost severity towards the native population." |
|||
Atrocities against the Jewish population in the conquered areas began almost immediately, with the dispatch of ''[[Einsatzgruppen]]'' (task groups) to round up Jews and shoot them. Local [[anti-semite]]s were encouraged to carry out their own [[pogrom]]s. In July 1941 [[Erich von dem Bach-Zalewski]]'s SS unit began to carry out more systematic killings, including the massacre of over 30,000 Jews at [[Babi Yar]]. By the end of 1941 there were more than 50,000 troops devoted to rounding up and killing Jews. The gradual industrialization of killing led to adoption of the [[Final Solution]] and the establishment of the [[Operation Reinhard]] extermination camps: the machinery of the [[Holocaust]]. In three years of occupation, between one and two million Soviet Jews were killed. Other ethnic groups were targeted for extermination, including the [[Roma people|Roma]] and [[Sinti]]; see [[Porajmos]]. |
|||
[[Image:Nazi german atrocities.jpg|thumb|left|Execution of Russian civilians by a shot in the back of the head]] |
|||
The massacres of Jews and other [[Ethnic minority|ethnic minorities]] were only a part of the deaths from the Nazi occupation. Many hundreds of thousands of Soviet civilians were executed, and millions more died from [[starvation]] as the Germans requisitioned food for their armies and fodder for their draft horses. As they retreated from Ukraine and Belarus in 1943–44, the German occupiers systematically applied a [[scorched earth]] policy, burning towns and cities, destroying infrastructure, and leaving civilians to starve or die of exposure. In many towns, the Germans also fought Soviet forces right within towns and cities with trapped civilians caught in the middle. Estimates of total civilian dead in the Soviet Union in the war range from seven million ([[Encyclopædia Britannica]]) to seventeen million (Richard Overy). |
|||
The Nazi ideology and the maltreatment of the local population and Soviet POWs encouraged [[Partisan (military)|partisan]]s fighting behind the front, motivated even anti-communists or non-Russian nationalists to ally with the Soviets, and greatly delayed the formation of German allied divisions consisting of Soviet POWs (see [[Vlasov army]]). These results and missed opportunities contributed to the defeat of the ''Wehrmacht''. |
|||
[[Image:Lost children russia about 1942.jpg|right|thumb|200px|Homeless Russian children in occupied territory (about 1942)]] |
|||
A Russian historian Vadim Erlikman has detailed Soviet losses totaling 26.5 million war related deaths. Military losses of 10.6 million include 7.6 million killed or missing in action and 2.6 million [[POW]] dead, plus 400,000 paramilitary and [[Soviet partisans|Soviet partisan]] losses. Civilian deaths totaled 15.9 million, which included 1.5 million from military actions; 7.1 million victims of Nazi [[genocide]] and reprisals; 1.8 million deported to Germany for [[forced labor]]; and 5.5 million [[famine]] and [[disease]] deaths. Additional famine deaths, which totaled 1 million during 1946-47, are not included here. These losses are for the entire territory of the USSR including territories annexed in 1939-40.[http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_m3955/is_n4_v46/ai_15654726] |
|||
[[Belarus]] lost a quarter of its pre-war population, including practically all its intellectual elite. Following bloody encirclement battles, all of the present-day Belarus territory was occupied by the Germans by the end of August 1941. The Nazis imposed a brutal regime, deporting some 380,000 young people for [[slave labour]], and killing hundreds of thousands of civilians more. More than 600 villages like [[Khatyn]] were burned with their entire population.[http://www.belarusguide.com/travel1/Khatyn.html] More than 209 cities and towns (out of 270 total) and 9,000 villages were destroyed. [[Himmler]] pronounced a plan according to which 3/4 of Belarusian population was designated to "eradication" and 1/4 of racially cleaner population (blue eyes, light hair) would be allowed to serve Germans as slaves. |
|||
Some recent reports raise the number of Belarusians who perished in War to "3 million 650 thousand people, unlike the former 2.2 million. That is to say not every fourth inhabitant but almost 40% of the pre-war Belarusian population perished (considering the present-day borders of Belarus)." [http://www.belarusguide.com/history1/WWII_partisan_resistance_in_Belarus.htm] |
|||
Sixty percent of Soviet [[POWs]] died during the war. Large numbers of Soviet POWs and forced laborers transported to Germany were on their return to the USSR (in many cases [[Operation Keelhaul|forcefully repatriated]] by the [[Western Allies]]) treated as traitors and deserters and were executed or deported to the Soviet prison camps. |
|||
The [[Soviet Union]] had not signed the [[Geneva Convention (1929)]]. However, a month after the German invasion in 1941, an offer was made for a reciprocal adherence to the [[Hague Conventions (1899 and 1907)|Hague convention]]. This 'note' was left unanswered by Third Reich officials <ref>Beevor, ''Stalingrad''. Penguin 2001 ISBN 0141001313 p60</ref>. |
|||
The official [[Poland|Polish]] government report of war losses prepared in 1947 reported 6,028,000 war victims out of a population of 27,007,000 ethnic [[Poles]] and [[Jews]]; this report excluded ethnic [[Ukrainians|Ukrainian]] and [[Belarusians|Belarusian]] losses. |
|||
==Industrial output== |
|||
[[Image:T34 1.jpg|frame|A [[T-34]] tank rolls off the line at the ''Krasnoye Sormovo'' Factory No. 112 in Gorki. The Soviet Union manufactured 58,000 T-34s during the war.]] |
|||
The Soviet victory owed a great deal to the ability of her war industry to outperform the German economy, despite the enormous loss of population and land. Stalin's [[five-year plan]]s of the 1930s had resulted in the industrialization of the Urals and central Asia. In 1941, the trains that shipped troops to the front were used to evacuate thousands of factories from Belarus and Ukraine to safe areas far from the front lines. |
|||
As the Soviet Union's manpower reserves ran low from 1943 onwards, the great Soviet offensives had to depend more on equipment and less on the expenditure of lives. The increases in production of war [[materiel]] were achieved at the expense of civilian living standards — the most thorough application of the principle of [[total war]] — and with the help of [[Lend-Lease]] supplies from the [[United Kingdom]] and the [[United States]]. The Germans, on the other hand, could rely on a large slave workforce from the conquered countries and Soviet [[POW]]s. |
|||
Germany's raw material production was higher than the Soviets' and her labour force was far greater, but the Soviets were more efficient at using what resources they had and chose to build low-cost, low-maintenance vehicles whilst the Germans built high-cost, high-maintenance vehicles. |
|||
Germany chose to build very expensive and very complicated vehicles and even though Germany produced many times more raw materials she could not compete with the Soviets on the quantity of military production (in 1943, the [[Soviet armored fighting vehicle production during World War II|Soviet Union manufactured 24,089 tanks]] to [[German armored fighting vehicle production during World War II|Germany's 19,800]]). The Soviets incrementally upgraded existing designs, and simplified and refined manufacturing processes to increase production. Meanwhile, German industry was forced to engineer more advanced but complex designs such as the [[Panther tank]], the [[King Tiger]] or the [[Elefant]]. |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
|||
|+ Summary of German and Soviet Raw Material production during the war<ref name="Russia's War">Richard Overy, ''Russia's War'', p. 155 and ''Campaigns of World War II Day By Day'', by Chris Bishop and Chris McNab, pp. 244-52.</ref> |
|||
|- |
|||
!rowspan="2"|Year |
|||
!colspan="2"|Coal<br />(million tonnes) |
|||
!colspan="2"|Steel<br />(million tonnes) |
|||
!colspan="2"|Aluminium<br />(thousand tonnes) |
|||
!colspan="6"|Oil<br />(million tonnes) |
|||
|- |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|German |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|Soviet |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|German |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|Soviet |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|German |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|Soviet |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|German |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|Soviet |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|Italian |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|Hungarian |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|Romanian |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|Japanese |
|||
|- |
|||
!1941 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|315.5 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|151.4 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|28.2 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|17.9 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|233.6 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|– |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|5.7 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|33.0 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|0.12 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|0.4 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|5.5 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|- |
|||
|- |
|||
!1942 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|317.9 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|75.5 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|28.7 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|8.1 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|264.0 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|51.7 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|6.6 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|22.0 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|0.01 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|0.7 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|5.7 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|1.8 |
|||
|- |
|||
!1943 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|340.4 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|93.1 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|30.6 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|8.5 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|250.0 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|62.3 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|7.6 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|18.0 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|0.01 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|0.8 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|5.3 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|2.3 |
|||
|- |
|||
!1944 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|347.6 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|121.5 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|25.8 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|10.9 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|245.3 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|82.7 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|5.5 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|18.2 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|- |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|1 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|3.5 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|1 |
|||
|- |
|||
!1945<ref name="Soviet numbers">Soviet numbers for 1945 are for the whole of 1945 even after the war was over.</ref> |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|– |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|149.3 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|– |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|12.3 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|– |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|86.3 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|1.3 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|19.4 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|- |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|- |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|- |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|0.1 |
|||
|} |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
|||
|+ Summary of Axis and Soviet Tank and Self-<br />propelled Gun production during the war<ref name="Russia's War"/> |
|||
|- |
|||
!rowspan="2"|Year |
|||
!colspan="5"|Tanks and self-<br />propelled guns |
|||
|- |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|Soviet |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|German |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|Italian |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|Hungarian |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|Japanese |
|||
|- |
|||
!1941 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|6,590 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|5,200<ref name="German tank numbers">German figures for 1941 and 1942 include tanks only. (Self-propelled guns cost 2/3 of a tank (mainly because they have no turret) and were more appropriate in a defensive role. The Germans therefore favored their production in the second half of the war.)</ref> |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|595 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|- |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|595 |
|||
|- |
|||
!1942 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|24,446 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|9,300<ref name="German tank numbers"/> |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|1,252 |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff" rowspan="3"|500 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|557 |
|||
|- |
|||
!1943 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|24,089 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|19,800 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|336 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|558 |
|||
|- |
|||
!1944 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|28,963 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|27,300 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|- |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|353 |
|||
|- |
|||
!1945<ref name="Soviet numbers"/> |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|15,400 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|– |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|- |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|- |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|137 |
|||
|} |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
|||
|+ Summary of Axis and Soviet Aircraft production during the war<ref name="Russia's War"/> |
|||
|- |
|||
!rowspan="2"|Year |
|||
!colspan="6"|Aircraft |
|||
|- |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|Soviet |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|German |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|Italian |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|Hungarian |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|Romanian |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|Japanese |
|||
|- |
|||
!1941 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|15,735 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|11,776 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|3,503 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|- |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff" rowspan="5"|1,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|5,088 |
|||
|- |
|||
!1942 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff|25,436 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|15,556 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|2,818 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|6 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|8,861 |
|||
|- |
|||
!1943 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|34,845 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|25,527 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|967 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|267 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|16,693 |
|||
|- |
|||
!1944 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|40,246 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|39,807 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|- |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|773 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|28,180 |
|||
|- |
|||
!1945<ref name="Soviet numbers"/> |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|20,052 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|7,544 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|- |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|- |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|8,263 |
|||
|} |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
|||
|+ Summary Of German and Soviet Industrial Labour (including those classified as handworkers), and Summary of Foreign, Voluntary, Coerced and POW Labour<ref>''The Dictators: Hitler's Germany, Stalin's Russia'' by [[Richard Overy]] p. 498.</ref> |
|||
|- |
|||
!rowspan="2"|Year |
|||
!colspan="2"|Industrial Labour |
|||
!colspan="2"|Foreign Labour |
|||
!colspan="2"|Total Labour |
|||
|- |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|Soviet |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|German |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|Soviet |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|German |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|Total Soviet |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|Total German |
|||
|- |
|||
!1941 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|11,000,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|12,900,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|- |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|3,500,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|11,000,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|16,400,000 |
|||
|- |
|||
!1942 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|7,200,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|11,600,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|50,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|4,600,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|7,250,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|16,200,000 |
|||
|- |
|||
!1943 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|7,500,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|11,100,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|200,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|5,700,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|7,700,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|16,800,000 |
|||
|- |
|||
!1944 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|8,200,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|10,400,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|800,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|7,600,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|9,000,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|18,000,000 |
|||
|- |
|||
!1945<ref name="Soviet numbers"/> |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|9,500,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|– |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|2,900,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|- |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|12,400,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|- |
|||
|} |
|||
It should be noted that the Axis allies Italy, Romania, Hungary and Bulgaria added to the German numbers. Two-thirds of Germany's [[Iron ore]], much needed for her military production, came from [[Sweden]]. Soviet production and upkeep was assisted by the [[Lend-Lease]] program from the United States and Britain. After the defeat at Stalingrad, Germany geared completely towards a war economy, as expounded in [[Goebbels]]' [[Sportpalast speech]], increasing production in subsequent years under [[Albert Speer]]'s astute direction, despite the intensifying [[Strategic bombing during World War II|Allied bombing campaign]]. |
|||
==Casualties== |
|||
{{see|World War II casualties|World War II casualties of the Soviet Union}} |
|||
From 1941 on, Stalin was willing to strike back against the [[Eastern Front (World War II)#Operation Barbarossa: Summer 1941|invading Axis forces]] at all costs and led the war with extreme brutality, including against his own soldiers.<ref name="Merridale, Ivan's War"> Catherine Merridale, ''Ivan's War, the Red Army 1939-1945'', London: Faber and Faber, 2005, ISBN 0-5712-1808-3</ref><ref name="Not so friendly">[http://www.rmc.ca/academic/conference/iuscanada/papers/goette_sovietpaper.pdf ''Not-So-Friendly Fire''], Queen’s University, Canada</ref> The Red Army took much higher casualties than any other military force during World War II, in part because of high manpower attrition and inadequate time for training.<ref>[http://www-cgsc.army.mil/carl/resources/csi/glantz2/glantz2.asp CSI Report No. 11]: Soviet Defensive Tactics at Kursk</ref> Faced with badly equipped [[infantry]] units barely capable of standing up against [[machine guns]], [[tanks]] and [[artillery]], the tactics of Soviet commanders were often based on mass infantry attacks, inflicting heavy losses on their own troops. This tactic was also used for clearing minefields, which were ‘attacked’ by waves of infantry soldiers in order to clear them.<ref>David Glantz, Barbarossa: Hitler's Invasion of Russia 1941 (2001) ISBN 0-7524-1979-X </ref><ref>David Glantz, Stumbling Colossus: The Red Army on the Eve of World War (1998) ISBN 0-7006-0879-6</ref><ref>[http://www.ess.uwe.ac.uk/genocide/reviewsw63.htm Review of "Stumbling Colossus"] </ref><ref name="Merridale, Ivan's War" /> In accordance with the orders of Soviet High Command, retreating soldiers or even soldiers who hesitated to advance faced being shot by rearguard [[SMERSH]] units: |
|||
[[Order № 270|Stalin’s order No 270]] of August 16, 1941, states that in case of retreat or surrender, all officers involved were to be shot on the spot and all enlisted men threatened with total annihilation as well as possible reprisals against their families.<ref name="Not so friendly"/>.<ref>[http://www.hrono.ru/dokum/194_dok/19410816.html Order No 270 in Russian language on hrono.ru] </ref><ref name="Merridale, Ivan's War" /> |
|||
The fighting involved millions of Axis and Soviet troops along the broadest land front in military history. It was by far the deadliest single [[Theatre (warfare)|theatre of war]] in World War II, with over 5 million deaths on the Axis Forces; Soviet military deaths were about 10.6 million (out of which 3.3 million Soviets died in German captivity<ref> Richard Overy, The Dictators </ref>), and estimated civilian deaths range from about 14 to 17 million. Over 11.4 million Soviet civilians, and another estimated 3.5 million civilians from the Annexed territories were killed.<ref>G. I. Krivosheev. ''Soviet Casualties and Combat Losses''. Greenhill 1997 ISBN 1-85367-280-7</ref> Soviet and Russian historiography often uses the so-called irretrievable casualties term. According to the [[Narkomat]] of Defence order (№ 023, February 4, 1944), the irretrievable casualties include killed, missed, those who died due to war-time or subsequent wounds, maladies and [[chilblain]]s and those who were captured. Also, the Nazis exterminated over 1 million Soviet Jews <ref name=autogenerated1>[[Martin Gilbert]]. ''Atlas of the Holocaust'' 1988 ISBN 0-688-12364-3</ref> and another 4.2 million Jews from the annexed territories which include over 3 million Polish Jews<ref name=autogenerated1 /> in the [[Holocaust]]. |
|||
The genocidal death toll was attributed to several factors, including brutal mistreatment of POWs and captured partisans by both sides, multiple atrocities by the Germans and the Soviets against the civilian population and each other, the wholesale use of weaponry on the battlefield against huge masses of infantry. The multiple battles, and most of all, the use of [[scorched earth]] tactics destroyed [[Agriculture|agricultural land]], infrastructure, and whole towns, leaving much of the population homeless and without food. |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
|||
|+ Military losses on the Eastern Front during World War II<ref>Rűdiger Overmans, ''Deutsche militärische Verluste im Zweiten Weltkrieg''. Oldenbourg 2000. ISBN 3-486-56531-1, [[Richard Overy]] The Dictators: Hitler's Germany and Stalin's Russia (2004), ISBN 0-7139-9309-X</ref> |
|||
|- |
|||
!colspan="5"|Forces fighting with the Axis |
|||
|- |
|||
! |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|Total Dead |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|[[Killed in action|KIA]]/[[Missing in action|MIA]] |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|POWs taken by the Soviets |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|POWs that died in Captivity |
|||
|- |
|||
!Greater Germany |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|4,300,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|4,000,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|3,300,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|374,000 |
|||
|- |
|||
!Soviet residents who joined German army |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|215,000+ |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|215,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|1,000,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|Unknown |
|||
|- |
|||
!Romania |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|281,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|81,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|500,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|200,000 |
|||
|- |
|||
!Hungary |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|300,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|100,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|500,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|200,000 |
|||
|- |
|||
!Italy |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|82,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|32,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|70,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|50,000 |
|||
|- |
|||
!Total |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|5,178,000+ |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|4,428,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|5,450,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|824,000 |
|||
|- |
|||
|} |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
|||
|+ Military losses on the Eastern Front during World War II<ref>Vadim Erlikman, ''Poteri narodonaseleniia v XX veke: spravochnik''. Moscow 2004. ISBN 5-93165-107-1; |
|||
Mark Axworthy, ''Third Axis Fourth Ally''. Arms and Armour 1995, p. 216. ISBN 1-85409-267-7</ref> |
|||
|- |
|||
!colspan="5"|Forces Fighting with the Soviet Union |
|||
|- |
|||
! |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|Total Dead |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|KIA/MIA |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|POWs taken by the Axis |
|||
!style="background:#ffffff"|POWs that died in captivity |
|||
|- |
|||
!Soviet |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|10,600,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|6,600,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|5,200,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|3,600,000 |
|||
|- |
|||
!Poland |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|24,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|24,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|Unknown |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|Unknown |
|||
|- |
|||
!Romania |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|17,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|17,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|80,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|Unknown |
|||
|-|- |
|||
!Bulgaria |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|10,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|10,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|Unknown |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|Unknown |
|||
|- |
|||
!Total |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|10,651,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|6,651,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|5,280,000 |
|||
|align="right" style="background:#ffffff"|3,600,000 |
|||
|- |
|||
|} |
|||
Total Soviet losses includes Deaths Partisans-250,000 and Deaths Militia-150,000 |
|||
[[Polish Armed Forces in the East]], initially consisting of Poles from Eastern Poland or otherwise in Soviet Union in 1939-1941, began fighting alongside the Red Army in 1943, and grew steadily as more Polish territory was liberated from the Nazis in 1944-1945. |
|||
When the Axis countries of Eastern Europe were occupied by the Soviets, they were forced to change sides and declare war on Germany. (see [[Allied Commission]]s). |
|||
Some of the Soviet citizens would side with the Germans and join [[Andrey Vlasov]]'s [[Russian Liberation Army]]. Most of those who joined were Russian POWs. Most who joined hated communism and actually saw the Nazis as liberators from communism. These men were primarily used in the Eastern Front but some were assigned to guard the beaches of [[Normandy]]. |
|||
The other main group of men joining the German army were citizens of the Baltic countries annexed by the Soviet Union in 1940 or from [[Western Ukraine]]. They fought in their own Waffen-SS units. |
|||
A comparison of the losses demonstrates the cruel treatment of the Soviet POWs by the Nazis. Most of the Axis POWs were released from captivity after the war, but the fate of the Soviet POWs differed markedly. Nazi troops who captured Red Army soldiers frequently shot them in the field or shipped them to [[concentration camp]]s and executed them. Hitler's notorious [[commissar order|Commissar Order]] implicated all the German armed forces in the policy of war crimes. |
|||
<!-- 3. [http://www.duel.ru/200517/?17_7_1 Duel.ru Владимир Литвиненко. ''Были ли потери Красной Армии в Великой Отечественной войне чрезмерными?''] --> |
|||
==See also== |
|||
[[Image:Victory Park (Moscow).jpg|thumb|250px|Victory Alley on [[Poklonnaya Hill]] in [[Moscow]]]] |
|||
* [[Historiography of World War II]] |
|||
* [[Timeline of the Eastern Front of World War II]] |
|||
* [[List of military operations on the Eastern Front of World War II]] |
|||
* [[Operation Silberfuchs]] – Axis attack on the Soviet Arctic |
|||
* [[Manchurian Strategic Offensive Operation]] – the Soviet campaign against [[Japan]] in [[Manchuria]], [[Inner Mongolia]], [[Korea]], [[Sakhalin]] and the [[Kurile Islands]] |
|||
* [[Captured German equipment in Soviet use in Eastern front]] |
|||
* [[Voenno-vozdushniye Sily]] – Soviet Air Force in World War II |
|||
* [[Morskaya Aviatsiya]] – Soviet Naval Air Service in World War II |
|||
* [[Women in the Russian and Soviet military]] |
|||
* [[Occupation of Belarus by Nazi Germany]] |
|||
* [[Italian war in Soviet Union, 1941-1943]] |
|||
** [[Alpini#World War II|The Italian Alpini infantry corps in Russia]] |
|||
* [[Pobediteli]] – Russian project celebrating the 60th anniversary of World War II |
|||
* [[The Battle of Russia]] – film from the ''[[Why We Fight]]'' propaganda film series |
|||
==Notes== |
|||
{{reflist}} |
|||
===References=== |
|||
* [[Antony Beevor|Beevor, Antony]]. ''Berlin: The Downfall 1945'', Penguin Books, 2002, ISBN 0-670-88695-5 |
|||
* Ziemke, Earl F. ''Battle For Berlin: End Of The Third Reich'', NY:Ballantine Books, London:Macdomald & Co, 1969. |
|||
*Ziemke, Earl F. "''[http://www.globalsecurity.org/military/library/report/other/us-army_germany_1944-46_index.htm#contents The U.S. Army in the occupation of Germany 1944-1946]''" Center of Military History, United States Army, Washington, D. C., 1990, Library of Congress Catalog Card Number 75-619027 |
|||
**[http://www.globalsecurity.org/military/library/report/other/us-army_germany_1944-46_ch15.htm CHAPTER XV: The Victory Sealed: Surrender at Reims] |
|||
==Bibliography== |
|||
* Anderson, Dunkan, et al. ''[http://books.google.com/books?vid=ISBN076030923X&id=iHh4Z0Cps08C&pg=PP1&lpg=PP1&dq=076030923X&sig=bxdcoaGKpklOS1hywSwpOvq7l4I The Eastern Front: Barbarossa, Stalingrad, Kursk and Berlin (Campaigns of World War II)]''. London: Amber Books Ltd., 2001. ISBN 0-7603-0923-X. |
|||
* [[Antony Beevor|Beevor, Antony]], and Artemis Cooper. ''Stalingrad: The Fateful Siege: 1942-1943''. New York: Penguin Books Ltd., 1998. ISBN 0140284583. |
|||
* Beevor, Antony. ''Berlin: The Downfall 1945''. New York: Penguin Books Ltd., 2004. ISBN 0141017473. |
|||
* Erickson, John. ''The Road to Stalingrad''. New York: Orion Publishing Group, Ltd., 2007. ISBN 0304365416. |
|||
* Erickson, John. ''The Road to Berlin''. New York: Orion Publishing Group, Ltd., 2007. ISBN 978-0304365401. |
|||
* Erickson, John, and David Dilks. ''Barbarossa, the Axis and the Allies''. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press, 1995. ISBN 0748605045. |
|||
* [[David Glantz|Glantz, David]], and Jonathan M. House. ''When Titans Clashed: How the Red Army stopped Hitler''. Lawrence, Kansas: University Press of Kansas, Reprint edition, 1998. ISBN 0700608990. |
|||
* Glantz, David, ''[http://www.strom.clemson.edu/publications/sg-war41-45.pdf The Soviet‐German War 1941–45]: Myths and Realities: A Survey Essay''. |
|||
* [[Heinz Guderian|Guderian, Heinz]]. ''[[Panzer Leader (book)|Panzer Leader]]'', Da Capo Press Reissue edition. New York: Da Capo Press, 2001. ISBN 0-306-81101-4. |
|||
* [[Max Hastings|Hastings, Max]]. ''Armageddon: The Battle for Germany, 1944-1945'', Vintage Books USA, 2005. ISBN 0375714227 |
|||
* [[David Irving|Irving, David]]. ''Hitler's War'', Reissue edition. Avon Books, 1990. ISBN 0380758067. |
|||
* [[Basil Liddell Hart|Liddell Hart, B.H.]] ''History of the Second World War''. United States of America: De Capo Press, 1999. ISBN 0306809125. |
|||
* [http://www.pen-and-sword.co.uk/?author_id=808 Lubbeck, William] and David B. Hurt. ''[http://www.pen-and-sword.co.uk/?product_id=1457 At Leningrad's Gates: The Story of a Soldier with Army Group North]'', Philadelphia: Casemate, 2006. ISBN 1-932033-55-6. |
|||
* Müller, Rolf-Dieter and Gerd R. Ueberschär. ''[http://www.questia.com/PM.qst?a=o&d=22785646 Hitler's War in the East, 1941-1945: A Critical Assessment]''. Berghahn Books, 1997. ISBN 1-57181-068-4. |
|||
* [[Richard Overy|Overy, Richard]]. ''Russia's War: A History of the Soviet Effort: 1941–1945'', New Edition. New York: Penguin Books Ltd., 1998. ISBN 0140271694. |
|||
* Seaton, Albert. ''The Russo-German War, 1941–1945'', Reprint edition. Presidio Press, 1993. ISBN 0891414916. |
|||
* [[F. W. Winterbotham|Winterbotham, F.W.]] ''The Ultra Secret'', New Edition. Orion Publishing Group Ltd., 2000. ISBN 0752837516. |
|||
==External links== |
|||
{{WWIITheatre}} |
|||
* [http://www.bbc.co.uk/history/worldwars/wwtwo/soviet_german_war_01.shtml Prof Richard Overy writes a summary about the eastern front for the BBC] |
|||
* [http://www.borodulincollection.com/war/english/index.html Rarities of the USSR photochronicles. Great Patriotic War 1941-1945] Borodulin Collection. Excellent set of war photos |
|||
* [http://www.iremember.ru/index_e.htm Russian veterans of World War II memories(In English and Russian)] |
|||
* [http://www.onwar.com/maps/wwii/eastfront1/index.htm OnWar maps of the Eastern Front] |
|||
* [http://www.wilhelm-radkovsky.de Memories of Leutnant d.R. Wilhelm Radkovsky 1940-1945] Experiences as a German soldier on the Eastern and Western Front |
|||
* [http://english.pobediteli.ru/ Pobediteli: Eastern Front flash animation] (photos, video, interviews, memorials. Written from a Russian perspective) |
|||
* [http://www.feldgrau.com/index.html Feldgrau.com] The German Armed Forces 1919-1945 |
|||
* [http://www.daswolf.co.uk/index.php?p=Eastern+Front+Chronology Information about the Eastern front up to September 1943] |
|||
* [http://rkkaww2.armchairgeneral.com/ RKKA in World War II] |
|||
* [http://rodohforum.yuku.com/topic/6101 27 Million] |
|||
* [http://rodohforum.yuku.com/topic/2558?page=1 Pictures of German Occupation in the USSR] |
|||
* [http://allworld.startlogic.com/Small-Unit-Actions-During-German-Campaign-in-Russia.html Small Unit Actions During German Campaign in Russia] German and Soviet tactics explained, written by former German commanders in the East |
|||
* [http://www.armchairgeneral.com/rkkaww2/maps.htm Armchair General maps, year by year] |
|||
<br> |
|||
'''Østfronten''' er navnet på den række af slag under [[2. verdenskrig]], som blev ført på den tyske østfront. Ordet betegner derfor på én gang den øjeblikkelige frontlinje på en given dato og helheden af de kampe, der blev indledt ved Tysklands angreb på Sovjetunionen. |
|||
== Operation "Barbarossa" == |
|||
[[Image:Eastern Front 1941-06 to 1941-12.png|thumb|300px|Operation Barbarossa: den tyske invasion af [[Sovjetunionen]], [[21. juni]] [[1941]] til [[5. december]] [[1941]]: |
|||
{{legend|#fff8d5|til 9. juli 1941}} |
|||
{{legend|#ffd2b9|til 1. september 1941}} |
|||
{{legend|#ebd7ff|til 9. september 1941}} |
|||
{{legend|#ccffcd|til 5. december 1941}}]] |
|||
{{uddybende|Operation Barbarossa}} |
|||
Den [[22. juni]] [[1941]] igangsatte tyskerne en overraskelsesinvasion af Sovjetunionen under betegnelsen [[operation Barbarossa]]. De første uger af invasionen var katastrofale for den sovjetiske hær på trods af, at [[Stalin]] flere gange var blevet advaret om invasionen, dels fra hans egne efterretninger og dels fra englænderne, der havde data af høj kvalitet fra [[Enigma]]. Store hærenheder blev omringet og overgav sig, og luftvåbnet blev nærmest udslettet på jorden. Det var dog ikke alene tyske hærenheder, der udgjorde invasionsstyrken. Italienske, [[Ungarn|ungarske]] og [[Rumænien|rumænske]] tropper var også en del af felttoget. |
|||
Situationen i [[Finland#Historie|Finland]] var meget speciel. Finland erklærede sig først neutral, men havde både tyske og sovjetiske tropper på sit område. Finland var velforberedt på en krig på tysk side, da Sovjetunionen angreb det den [[25. juni]]. Den følgende konflikt [[1941]]-[[1944]] har fået navnet [[fortsættelseskrigen]] med henvisning til, at den var en fortsættelse af [[Vinterkrigen]]. |
|||
Operation Barbarossa havde en række svage punkter. Alvorligst var den [[Logistik|logistiske]] situation. I sidste ende var det logistikken, som var afgørende for den tyske hærs muligheder. De enorme distancer i Sovjetunionen indebar, at tyskerne ikke kunne avancere længere, end deres forsyningslinjer tillod. Da det tyske angreb stoppede foran [[Moskva]] den [[5. december]] [[1941]], var det umuligt at drive tropperne længere fremad. Der var simpelthen ikke forsyninger nok, som nåede frem til fronten, til at et ordentligt forsvar kunne organiseres for slet ikke at tale om offensive operationer. Tidsplanen for det tyske angreb byggede på, at den sovjetiske hær ville kollapse, før den russiske vinter satte ind. At dette ikke skete, påvirkede i høj grad de tyske planer. Fedtet i lejerne på de tyske kampvogne frøs, og tyskerne måtte tage vintertøj fra døde russiske soldater for at overleve. Hvis tyskerne havde omringet Moskva, havde russerne måske bedt om våbenstilstand, da Moskva var knudepunkt for alle de sovjetiske jernbaner, og landet havde ikke tid eller lastbiler nok til at forbinde jernbanerne bag en front øst for Moskva. |
|||
Under deres lange tilbagetrækning anvendte de russiske styrker [[den brændte jords taktik]]. De brændte afgrøder og ødelagde bygninger og anlæg, efterhånden som de trak sig tilbage for de fremadstormende tyske tropper. Dette forøgede drastisk de tyske forsyningsproblemer, samtidig med at tabene på grund af den frygtede russiske kulde og russiske modangreb steg kraftigt. Flere hundrede tusinde soldater døde på grund af disse faktorer. |
|||
På trods af problemer med yderligere at fremskynde deres fremrykning havde tyskerne på dette tidspunkt erobret et enormt område. Tilbageerobringen af dette område kom til at koste Sovjetunionen dyrt og varede indtil sent i 1944. |
|||
== Belejringen af Leningrad == |
|||
{{uddybende|Belejringen af Leningrad}} |
|||
Tyskernes store erobringer bragte dem også tæt på [[Leningrad]] (nu [[Sankt Petersborg]]), og udløste hermed en af krigens tragedier – belejringen af Leningrad. Finske tropper stødte frem mod byen fra nord og den tyske værnemagt fra syd. Den finske øverstbefalende, [[Carl Gustaf Mannerheim]], var stoppet ved floden [[Svir]] og afstod fra at angribe byen. Hitler derimod beordrede, at byen skulle "fjernes fra jordens overflade", sammen med hele sin befolkning. Byen blev derfor ikke stormet. Den tyske hær omringede i stedet byen næsten fuldstændigt for at sulte dens befolkning ihjel, samtidig med at bombefly og artilleri sendte en regn af bomber og granater over byen. Cirka en million civile døde under belejringen af Leningrad – 800.000 af sult. Belejringen varede 900 dage, og da den var mest omfattende, var den eneste vej ind og ud af byen over den tilfrosne sø [[Ladoga]], midt imellem de tyske og finske linjer. Man anlagde endog en jernbane på isen. På et tidspunkt brækkede isen, og et langt stykke jernbaneskinner forsvandt i dybet. Ingen anden materiel skade. |
|||
[[Billede:Yalta summit 1945 with Churchill, Roosevelt, Stalin.jpg|right|300px|thumb|'''De allierede ledere''' ved [[Jaltakonferencen]] [[4. februar|4.]] til [[11. februar]] 1945 <br /> (siddende): Premierminister [[Winston Churchill]] (UK), præsident [[Franklin D. Roosevelt]] (US) og formand [[Josef Stalin]] (USSR). Stående længst til venstre ses den sovjetiske udenrigsminister [[Molotov]]]] |
|||
== Kampen om Stalingrad == |
|||
{{uddybende|Slaget om Stalingrad}} |
|||
Da vinteren 1941-42 var overstået, begyndte den tyske hær at forberede yderligere offensive aktioner. Frem for en offensiv mod Moskva blev prioriteringen ændret til retning mod [[Stalingrad]] (nu [[Volgograd]]) ved floden [[Volga]] og mod [[Kaukasus]]. Stalingrad (vest for floden) blev erobret med undtagelse af nogle små modstandslommer, men kampagnen tog en katastrofal vending for de tyske styrker. |
|||
Ubeslutsomhed hos Adolf Hitler, uenighed blandt højtstående tyske officerer og udstrakte forsyningslinjer kombineret med længerevarende bykampe i Stalingrad gjorde den tyske stilling udsat. I et forsøg på at fremskynde byens fald blev store tyske inklusive reserver og pansertropper, der fungerede som infanteri, indsat i selve byen. De meget lange flanker ved [[Don]]-floden blev herefter delvist forsvaret af forholdsvis svage rumænske, italienske og ungarske styrker. Efter en sovjetisk modoffensiv ([[Operation Uranus]]) i november 1942, blev den tyske 6. armé sammen med det 4. panserkorps afskåret. Sult, mangel på mad og ammunition gjorde at "kedlen" gradvis blev mindre og mindre. Hitler beordrede, at ingen tyske tropper måtte overgive sig: De skulle kæmpe til sidste mand og sidste patron, og han udnævnte symbolsk [[generalfeltmarskal Paulus|general Paulus]] til generalfeltmarskal, da ingen tysk soldat med den rang tidligere havde overgivet sig. Dette skete alligevel i begyndelsen af februar 1943. Begge sider led store tab i slaget om Stalingrad, som blev historiens hidtil største og mest blodige slag. Det anslås, at 2 millioner mennesker døde i slaget om Stalingrad, herunder 500.000 civile. |
|||
== Kampvognsslaget ved Kursk == |
|||
{{uddybende|Panserslaget ved Kursk}} |
|||
Efter Stalingrad blev det tyske initiativ svagere. Sovjet formåede dog ikke at gribe dette fuldt ud, idet en offensiv, [[Operation Zitadelle]], i sommeren 1943 under [[von Manstein]] stoppede det sovjetiske angreb. Slaget ved [[Kursk]] blev det største kampvognsslag, historien endnu havde set, og den blev tyskernes sidste større offensiv på østfronten. Gode efterretninger havde forberedt Sovjetunionen på det tyske modangreb, og man havde forberedt massive forsvarslinjer omkring Kursk. Russerne var herefter i offensiven, indtil Berlin blev erobret i maj 1945, og krigen sluttede. |
|||
== Konsekvenser == |
|||
Sovjetunionen kom til at bære den største del af omkostningerne ved 2. verdenskrig. Den anden front i Europa, der skulle aflaste østfronten, blev først realiseret på D-dag (bortset fra invasionen af Italien). Landet havde derfor flere ofre end samtlige øvrige lande tilsammen: cirka 27 millioner døde, heraf mere end 13 millioner civile. Mange civile blev myrdet i erobrede byer af tyskerne, der dels anså befolkningen for at være undermennesker, dels havde planer om at genbefolke landet med tyskere. |
|||
Sovjetunionen kæmpede dog ikke alene. Britiske og amerikanske forsyningskonvojer sejlede under stor risiko forsyninger til landet. Tyske styrker blev anvendt til at beskytte kystlinjer mod angreb, som aldrig blev iværksat og til at bemande antiluftskyts over hele Europa. Sovjetunionen tog heller ikke aktivt del i søslagene, bombeoffensiverne og sejren over Japan. Den 8. august 1945 angreb Sovjetunionen dog med tre armeer, som led i Jalta-aftalen, de japanske styrker i Manchuriet, og på to uger nedkæmpede Den Røde Hær en million japanske tropper. |
|||
{{Link FA|fi}} |
|||
{{Link FA|ro}} |
|||
{{Link FA|sr}} |
|||
{{Link FA|ko}} |
|||
[[Kategori:2. verdenskrig]] |
|||
[[ca:Front Oriental de la Segona Guerra Mundial]] |
|||
[[cs:Východní fronta 1941-1945]] |
|||
[[de:Ostfront (Zweiter Weltkrieg)]] |
|||
[[el:Μεγάλος Πατριωτικός Πόλεμος]] |
|||
[[en:Eastern Front (World War II)]] |
|||
[[es:Frente Oriental (Segunda Guerra Mundial)]] |
|||
[[et:Idarinne (Teine maailmasõda)]] |
|||
[[eu:Ekialdeko Frontea Bigarren Mundu Gerran]] |
|||
[[fi:Itärintama (toinen maailmansota)]] |
|||
[[fr:Front de l'Est (Seconde Guerre mondiale)]] |
|||
[[hi:महान देशभक्तिपूर्ण युद्ध]] |
|||
[[id:Front Timur (Perang Dunia II)]] |
|||
[[it:Fronte orientale (seconda guerra mondiale)]] |
|||
[[ja:東部戦線]] |
|||
[[ko:동부 유럽 전선 (제2차 세계 대전)]] |
|||
[[nl:Oostfront (Tweede Wereldoorlog)]] |
|||
[[no:Østfronten (andre verdenskrig)]] |
|||
[[oc:Front de l'Èst]] |
|||
[[pl:Front wschodni (II wojna światowa)]] |
|||
[[ro:Frontul de Răsărit (Al Doilea Război Mondial)]] |
|||
[[ru:Восточноевропейский театр военных действий Второй мировой войны]] |
|||
[[sr:Источни фронт у Другом светском рату]] |
|||
[[sv:Östfronten under andra världskriget]] |
|||
[[th:แนวรบด้านตะวันออก (สงครามโลกครั้งที่สอง)]] |
|||
[[tr:Doğu Cephesi (İkinci Dünya Savaşı)]] |
|||
[[vi:Chiến tranh Xô-Đức]] |
|||
[[zh:东方战线]] |
|||
Versionen fra 12. jan. 2009, 21:07
The Eastern Front of World War II (tysk: die Ostfront 1941-1945 [3], der Rußlandfeldzug 1941-1945 (Russian campaign) or der Ostfeldzug 1941-1945 (Eastern Campaign)[4]) was a theatre of war between the German Reich and the Soviet Union which encompassed central and eastern Europe from June 22, 1941 to May 9, 1945. Nazi propaganda dubbed the conflict The Crusade against Bolshevism. In all Soviet and the majority of Russian sources, the conflict in Eastern Europe is referred to as the Great Patriotic War, but sometimes that phrase also includes operations against Japan in 1945. Some scholars of the conflict use the term Russo-German War, while others use Soviet-German War, Nazi-Soviet War, German-Soviet War, or Axis-Soviet War.
It was the largest theatre of war in history and was notorious for its unprecedented ferocity, destruction, and immense loss of life. It bore the bulk of the Holocaust, and stands unparalleled in terms of the volume of scholarly analysis and cultural depictions it generated (films, books, video games etc.). More people fought and died on the Eastern Front than in all other theatres of World War II combined. With over 30 million dead, many of them civilians, the Eastern Front has been called a war of extermination. It resulted in the destruction of the Third Reich, the partition of Germany and the rise of the Soviet Union as a military and industrial superpower.
The series of events preceding the opening of the Eastern Front included the invasion of Poland in 1939 by Nazi Germany and the resulting fourth partition of Poland when the Soviet Union used the invasion as a pretext to annex the eastern regions of the country, populated mostly by Ukrainians and Belarussians, as outlined in the secret codicil to the August 1939 Soviet-German non-aggression pact, which also paved the way for the 1940 Occupation of Baltic states and the occupation of Bessarabia.
This article, however, concentrates on the much larger conflict fought from June 1941 to May 1945, in which the two principal belligerent powers were Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union. The Soviet-Finnish Continuation War may be considered the northern flank of the Eastern Front. In addition, the joint German-Finnish operations across the northernmost Finnish-Soviet border and in the Murmansk region are considered part of the Eastern Front.
Forces
The war was fought between the German Reich, its allies, and many pro-Nazi volunteers from occupied states, against the Soviet Union, and eventually its allies of the British Commonwealth, France and the United States. The conflict began on 22 June 1941 as part of the Operation Barbarossa Offensive, when Axis forces crossed the borders, described in the German-Soviet Nonaggression Pact, thereby invading the Soviet Union. The war ended on 9 May 1945, when Germany's armed forces surrendered unconditionally following the Berlin Offensive, a strategic operation executed by the Red Army, also known as the Battle of Berlin.
The states that provided forces and other resources for the German war effort included the Axis Powers — foremost Italy, Romania, Hungary, and pro-Nazi Slovakia and Croatia. The anti-Soviet Finland, which had fought two conflicts with the Soviet Union, also joined the Offensive. The Wehrmacht forces were also assisted by anti-Communist partisans in places like Western Ukraine, the Baltic states and later Crimean Tatars. Among the most prominent volunteer army formations was the Spanish Blue Division, sent by Spanish dictator Francisco Franco to keep his ties to the Axis intact.
The Soviet Union offered support to the partisans in many Wehrmacht-occupied countries in Eastern Europe, notably those in Slovakia, Poland and the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. In addition the Polish Armed Forces in the East, particularly the First and Second Polish armies, were armed and trained, and would eventually fight alongside the Red Army. The Free French forces also contributed to the Red Army by formation of GC3 (Groupe de Chasse 3 or 3rd Fighter Group) unit to fulfill the commitment of Charles de Gaulle, leader of the Free French, who thought that it was important for French servicemen to serve on all fronts. British and Commonwealth forces contributed directly to the fighting on the Eastern Front through their service in the convoys and training Red Air Force pilots, as well as in provision of early materiel and intelligence support. The later massive materiel support of the Lend-Lease by the United States and Canada played a significant part particularly in the logistics of the war.
Ideologies
Adolf Hitler had argued in his autobiography Mein Kampf for the necessity of Lebensraum, acquiring new territory for German settlement in Eastern Europe. He envisaged settling Germans there as a master race, while deporting most of the inhabitants to Siberia and using the remainder as slave labour.
To hard line Nazis in Berlin, (like Himmler[5]) the war against the Soviet Union was one of a struggle of Fascism against Communism, and the Aryan race against the "inferior" Slavic race. Hitler referred to it in unique terms, calling it a "war of annihilation", one in which the Soviet Union was to be utterly destroyed and the populations of Eastern Europe and Russia were to be enslaved and exterminated. This would further German expansion and provide for the colonization of Eastern Europe and Western Russia. The plan was called the Generalplan Ost. In addition, the Nazis also sought to wipe out the large Jewish population of Eastern Europe[6] as part of the Holocaust.
After the great purge of the 1930s, Hitler saw the Soviet Union as militarily weak and ripe for conquest: "We have only to kick in the door and the whole rotten structure will come crashing down."[7] Thus, another short Blitzkrieg was expected, no serious preparations for warfare in winter, or prolonged over years, were made. In the aftermath of the Battle of Stalingrad in 1943 and the resulting dire German military situation, Hitler and Nazi propaganda proclaimed the war to be a German defense of European (Western) Civilization against destruction by the vast "Bolshevik hordes" that were pouring into Europe.
Joseph Stalin's vision also included the occupation of foreign countries: using the occasion of world attention drawn to the Western Front, Soviet Union occupied the three Baltic countries and Bessarabia in 1940, thus gaining a place d'arme in case of a possible war with Hitler-Germany. Soviet active participation in the 1939 invasion of Poland should also not be underestimated.
Results
The Eastern Front was by far the largest and bloodiest theatre of World War II. It is generally accepted as being the deadliest conflict in human history, with over 30 million killed as a result. It involved more land combat than all other World War II theatres combined. The distinctly brutal nature of warfare on the Eastern Front was exemplified by an often willful disregard for human life by both sides. It was also reflected in the ideological premise for the war, which also saw a momentous clash between two directly opposed and radical ideologies.
Aside from the ideological conflict, the mindframe of the leaders of Germany and the Soviet Union, Hitler and Stalin respectively, contributed to the escalation of terror and murder on an unprecedented scale. Stalin and Hitler both disregarded human life in order to achieve their goal of victory. This included terrorization of their own people, as well as mass deportation (planned, in the case of Germany) of entire populations. All these factors resulted in tremendous brutality both to combatants and civilians that found no parallel on the Western Front. According to the Time: "By measure of manpower, duration, territorial reach and casualties, the Eastern Front was as much as four times the scale of the conflict on the Western Front that opened with the Normandy invasion."[8]
The war inflicted huge losses and suffering upon the civilian populations of the affected countries. Behind the front lines, atrocities against civilians in German-occupied areas were routine, including the Holocaust. German and German-allied forces treated civilian populations with exceptional brutality, massacring villages and routinely killing civilian hostages. Both sides practiced widespread scorched earth tactics, but the loss of civilian lives in the case of Germany was incomparably smaller than that of the Soviet Union, in which at least 20 million civilians were killed by the Nazis. When the Red Army invaded Germany in 1944, many German civilians suffered from vengeance taken by Red Army soldiers (see Red Army atrocities). After the war, following the Yalta conference agreements between the Allies, the German populations of East Prussia and Silesia were displaced to the west of the Oder-Neisse Line, in what became one of the largest forced migrations of people in world history. The German minority scattered over large swaths of Eastern Europe was thus expelled and those who did not manage to leave were exterminated.
Much of the combat took place in or close by populated areas, and the actions of both sides contributed to massive loss of civilian life as well as a tremendous material damage. According to a summary, presented by Lieutenant General Roman Rudenko at the International Military Tribunal in Nuremberg, the property damage in the Soviet Union inflicted by the Axis invasion was estimated to a value of 679 billion rubles. The largest number of civilian deaths in a single city was 1.2 million citizens dead during the Siege of Leningrad. The combined damage consisted of complete or partial destruction of 1,710 cities and towns, 70,000 villages/hamlets, 2,508 church buildings, 31,850 industrial establishments, 40,000 miles of railroad, 4100 railroad stations, 40,000 hospitals, 84,000 schools, and 43,000 public libraries. Seven million horses, and 17 million sheep and goats were also slaughtered or driven off.[9]Wild fauna were also affected. Wolves and foxes fleeing westward from the killing zone, as the Russian army advanced 1943-45, were responsible for a rabies epidemic which spread slowly westwards, reaching the Channel coast in 1968.[10]
Background
Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact
The Molotov-Ribbentrop Non-Aggression Pact of August 1939 had established a non-aggression agreement between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union, and a secret protocol outlined how Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, and Romania would be divided between them. The two powers invaded and partitioned Poland in 1939. In November 1939 the Soviet Union waged the Winter War against Finland. And in June 1940, threatening to use force if its demands were not fulfilled, it won the diplomatic wars against Romania and three Baltic states allowing it to peacefully occupy Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania de facto while no western state regarded the annexation of these states de jure. The pact allowed for the return of the Ukrainian, Belarusian, and Moldavian territories in the north and northeastern regions of Romania (Northern Bucovina and Basarabia) to the Soviet Union.
The decision for war
For nearly two years the border was quiet while Germany conquered Denmark, Norway, France, The Low Countries, and the Balkans. Hitler had however always intended to renege on the pact with the Soviet Union and invade, and appears to have made the decision of when to do so in the spring 1940. Hitler believed that the Soviets would quickly capitulate after an overwhelming German offensive and that the war could largely end before the onset of the fierce Russian winter.
Some say Joseph Stalin was fearful of war with Germany or just did not expect Germany to start a two-front war, and was reluctant to do anything to provoke Hitler. Others say that Stalin was eager for Germany to be at war with other capitalist countries. Another viewpoint is that Stalin expected war in 1942 (the time when all his preparations would be complete) and stubbornly refused to believe its early arrival.[11]
British historians Alan S. Milward and W. Medicott show that Nazi Germany--unlike Imperial Germany--was prepared for only a short-term war (Blitzkrieg).[kilde mangler] According to Andreas Hillgruber, without the necessary supplies from the USSR and the strategic security in the East, Germany could not have succeeded in the West. Had the Soviets joined the Anglo-French blockade, the German war economy would have been starved. With its own raw materials in September 1939, Germany could have been supplied for a mere 9 to 12 months.[kilde mangler]
Even though Germany had been assembling very large numbers of troops in eastern Poland and making repeated reconnaissance flights over the border, Stalin ignored the warnings of his own as well as foreign intelligence. Moreover, on the very night of the invasion, Soviet troops received a directive undersigned by Marshal Semyon Timoshenko and General of the Army Georgy Zhukov that ordered (as demanded by Stalin): "do not answer to any provocations" and "do not undertake any actions without specific orders". The German invasion therefore caught the Soviet military and leadership largely by surprise, even though Stalin did receive a message from his intelligence detailing information on the attack.
For Soviet preparations, see Operation Barbarossa: Soviet preparations.
Conduct of operations
While German historians do not apply any specific periodisation to the conduct of operations on the Eastern Front, all Soviet and Russian historians divide the war against Germany and its allies into three periods, which are further subdivided into the major Campaigns of the Theatre of war:
1. First period of World War II (russisk: Первый период Великой Отечественной войны) (22 June 1941 - 18 November 1942)
- Summer-Autumn Campaign (russisk: Летне-осенняя кампания 1941 г.) (22 June - 4 December 1941)
- Winter Campaign of 1941-42 (russisk: Зимняя кампания 1941/42 г.) (5 December 1941 - 30 April 1942)
- Summer-Autumn Campaign (russisk: Летне-осенняя кампания 1942 г.) (1 May - 18 November 1942)
2. Second period of World War II (russisk: Второй период Великой Отечественной войны) (19 November 1942 - 31 December 1943)
- Winter Campaign of 1942-43 (russisk: Зимняя кампания 1942-1943 гг.) (19 November 1942 - 3 March 1943)
- Summer-Autumn Campaign of 1943 (russisk: Летне-осенняя кампания 1943 г.) (1 July - 31 December 1943)
3. Third period of World War II (russisk: Третий период Великой Отечественной войны) (1 January 1944 - 9 May 1945)
- Winter-Spring Campaign (russisk: Зимне-весенняя кампания 1944 г.) (1 January - 31 May 1944)
- Summer-Autumn Campaign of 1944 (russisk: Летне-осенняя кампания 1944 г.) (1 June - 31 December 1944)
- Campaign in Europe during 1945 (russisk: Кампания в Европе 1945 г.) (1 January - 9 May 1945)
Excellent analytical works in English written on the history of the combat operation on the Eastern front in the past 20 years include those by David Glantz, which deal with large strategic as well as smaller scale operational and tactical aspects of the conflict.
Operation Barbarossa: Summer 1941
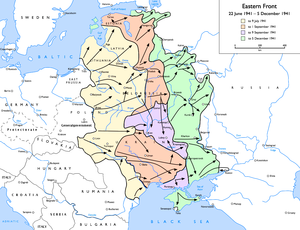
Operation Barbarossa began just before dawn on June 22, 1941. The Germans wrecked the wire network in all Soviet western military districts to undermine Soviet communications.[12] At 03:15 on 22 June 1941 ninety-nine (including fourteen panzer divisions and ten motorized) of 190 German divisions, deployed against the Soviet Union began the offensive from the Baltic to the Black seas. They were accompanied by ten Romanian divisions, nine Romanian and four Hungarian brigades.[13] On the same day the Baltic, Western and Kiev Special military districts were renamed to Northwestern, Western and Southwestern Fronts respectively.[12] For a month the offensive conducted on three axes was completely unstoppable as the panzer forces encircled hundreds of thousands of Soviet troops in huge pockets that were then reduced by slower-moving infantry armies while the panzers continued the offensive, following the Blitzkrieg doctrine. As part of this high tempo campaign the German air force began immediate attacks on Soviet airfields, destroying much of the forward-deployed Soviet Air Force airfield fleets consisting of largely obsolescent types before their pilots had a chance to leave the ground.
Army Group North's objective was Leningrad via the Baltic States. Comprising the 16th and 18th armies and the 4th Panzer Group, this formation advanced through Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia, and the Russian Pskov and Novgorod oblasts.
Army Group Centre comprised two panzer groups (2nd and 3rd), which advanced to the north and south of Brest-Litovsk and converged east of Minsk, followed by the 2nd, 4th, and 9th armies. The combined panzer force reached the Beresina River in just six days, 650 km (400 miles) from their start lines. The next objective was to cross the Dnieper river, which was accomplished by 11 July. Following that, their next target was Smolensk, which fell on 16 July, but the engagement in the Smolensk area halted the German advance until mid-September, effectively disrupting the blitzkrieg.
Army Group South, with 1st Panzer Group, 6th, 11th and 17th armies, was tasked with advancing through Galicia and into Ukraine. Their progress, however, was rather slow, and took heavy casualties in a major tank battle. With the corridor towards Kiev secured by mid-July, the 11th Army, aided by two Romanian armies, fought its way through Bessarabia towards Odessa. The 1st Panzer Group turned away from Kiev for the moment, advancing into the Dnieper bend (western Dnipropetrovsk Oblast). When it joined up with the southern elements of Army Group South at Uman, the Group captured about 100,000 Soviet prisoners in a huge encirclement.
As the Red Army withdrew behind the Dnieper and Dvina rivers, the Soviet Stavka turned its attention to evacuating as much of the western regions' industry as it could, dismantled and packed onto flatcars, away from the front line, re-establishing it in more remote areas of the Urals, Caucasus, Central Asia and south-eastern Siberia. Most civilians were left to make their own way East as only the industry-related workers could be evacuated with the equipment, and much of the population was left behind to the mercy of the invading forces.
With the capture of Smolensk, and the advance to the Luga river, Army groups Centre and North had completed their first major objective: to get across, and hold the "land bridge" between the Dvina and Dnieper. The advance to Moscow, now only 400 km (250 miles) away, could now begin.
The German generals argued for an immediate offensive towards Moscow, but Hitler overruled them, citing the importance of Ukrainian agricultural and mining resources, and heavy industry if under German possession, not to mention the massing of Soviet reserves in the Gomel area between Army Group Centre's southern flank and the bogged-down Army Group South's northern flank. The order was issued to 2nd Panzer Group to turn south and advance towards Kiev. This took the whole of August and into September, but when 2nd Panzer Group joined up with 1st Panzer Group at Lokhvitsa on 14 September 665,000 Soviet prisoners were captured as Kiev was surrendered on 19 September.
Immediately after the start of the German invasion, the NKVD massacred large numbers of prisoners in most of their prisons in Western Belarus and Western Ukraine, while the remainder was to be evacuated in death marches.[14] Most of them were political prisoners, imprisoned and executed without a trial.[15]
Moscow and Rostov: Autumn 1941
Hitler then decided to resume the advance to Moscow, re-designating the panzer groups as panzer armies for the occasion. Operation Typhoon, which was set in motion on 30 September, saw 2nd Panzer Army rush along the paved road from Orel (captured 5 October) to the Oka river at Plavskoye, while the 4th Panzer Army (transferred from Army Group North to Centre) and 3rd Panzer armies surrounded the Soviet forces in two huge pockets at Vyazma and Bryansk. Army Group North positioned itself in front of Leningrad and attempted to cut the rail link at Tikhvin to the east. Thus began the 900-day Siege of Leningrad. North of the Arctic Circle, a German-Finnish force set out for Murmansk but could get no further than the Zapadnaya Litsa River, where they settled down.
Army Group South pushed down from the Dnieper to the Sea of Azov coast, also advancing through Kharkov, Kursk, and Stalino. The 11th Army moved into the Crimea and had taken control of all of the peninsula by autumn (except Sevastopol, which held out until 3 July 1942). On 21 November the Germans took Rostov, the gateway to the Caucasus. However, the German lines were over-extended and the Soviet defenders counterattacked the 1st Panzer Army's spearhead from the north, forcing them to pull out of the city and behind the Mius River; the first significant German withdrawal of the war.

One last lunge on 15 November saw the Germans attempting to throw a ring around Moscow. On 27 November the 4th Panzer Army got within 30 km (19 miles) of the Kremlin when it reached the last tramstop of the Moscow line at Khimki, while the 2nd Panzer Army, despite its best efforts, failed to take Tula, the last Soviet city that stood in its way of the capital. After a meeting held in Orsha between the head of the Army General Staff, General Halder, and the heads of three Army groups and armies, it was decided to push forward to Moscow since it was better, as argued by head of Army Group Center, Field Marshal Fedor von Bock, for them to try their luck on the battlefield rather than just sit and wait while their opponent gathered more strength.
However, by 6 December it became clear that the Wehrmacht was too weak to capture Moscow and the attack was put on hold. Marshal Shaposhnikov thus began his counter-attack, employing freshly mobilized reserves[16], as well as some well-trained Far-Eastern divisions transferred from the east following the guarantee of neutrality from Japan.
Soviet counter-offensive: Winter 1941


During the autumn, Stalin had been transferring fresh and well-equipped Soviet forces from Siberia and the far east to Moscow (these troops had been stationed there in expectation of a Japanese attack, but Stalin's master spy Richard Sorge indicated that the Japanese had decided to attack Southeast Asia and the Pacific instead). On 5 December 1941, these reinforcements attacked the German lines around Moscow, supported by new T-34 tanks and Katyusha rocket launchers. The new Soviet troops were prepared for winter warfare, and they included several ski battalions. The exhausted and freezing Germans were routed and driven back between 100 and 250 km (60 to 150 miles) by 7 January 1942.
A further Soviet attack was mounted in late January, focusing on the junction between Army groups North and Centre between Lake Seliger and Rzhev, and drove a gap between the two German army groups. In concert with the advance from Kaluga to the south-west of Moscow, it was intended that the two offensives converge on Smolensk, but the Germans rallied and managed to hold them apart, retaining a salient at Rzhev. A Soviet parachute drop on German-held Dorogobuzh was spectacularly unsuccessful, and those paratroopers who survived had to escape to the partisan-held areas beginning to swell behind German lines. To the north, the Soviets surrounded a German garrison in Demyansk, which held out with air supply for four months, and established themselves in front of Kholm, Velizh, and Velikie Luki.
In the south the Red Army crashed over the Donets River at Izyum and drove a 100-km (60-mile) deep salient. The intent was to pin Army Group South against the Sea of Azov, but as the winter eased the Germans were able to counter-attack and cut off the over-extended Soviet troops in the Second Battle of Kharkov.
Don, Volga, and Caucasus: Summer 1942
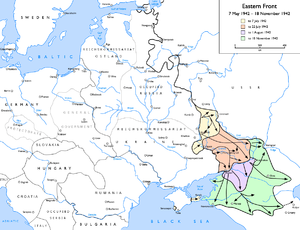
Although plans were made to attack Moscow again, on 28 June 1942, the offensive re-opened in a different direction. Army Group South took the initiative, anchoring the front with the Battle of Voronezh and then following the Don river southeastwards. The grand plan was to secure the Don and Volga first and then drive into the Caucasus towards the oilfields, but operational considerations and Hitler's vanity made him order both objectives to be attempted simultaneously. Rostov was recaptured on 24 July when 1st Panzer Army joined in, and then that group drove south towards Maikop. As part of this, Operation Shamil was executed, a plan whereby a group of Brandenburger commandos dressed up as Soviet NKVD troops to destabilise Maikop's defenses and allow the 1st Panzer Army to enter the oil town with little opposition.
Meanwhile, 6th Army was driving towards Stalingrad, for a long period unsupported by 4th Panzer Army, which had been diverted to help 1st Panzer Army cross the Don. By the time 4th Panzer Army had rejoined the Stalingrad offensive, Soviet resistance (comprising the 62nd Army under Vasily Chuikov) had stiffened. A leap across the Don brought German troops to the Volga on 23 August but for the next three months the Wehrmacht would be fighting the Battle of Stalingrad street-by-street.
Towards the south 1st Panzer Army had reached the Caucasian foothills and the Malka River. At the end of August Romanian mountain troops joined the Caucasian spearhead, while the Romanian 3rd and 4th armies were redeployed from their successful task of clearing the Azov littoral. They took up position on either side of Stalingrad to free German troops for the proper fighting. Mindful of the continuing antagonism between Axis allies Romania and Hungary over Transylvania, the Romanian army in the Don bend was separated from the Hungarian 2nd army by the Italian 8th Army. Thus all of Hitler's allies were involved — including a Slovakian contingent with 1st Panzer Army and a Croatian regiment attached to 6th Army.
The advance into the Caucasus bogged down, with the Germans unable to fight their way past Malgobek and to the main prize of Grozny. Instead they switched the direction of their advance to approach it from the south, crossing the Malka at the end of October and entering North Ossetia. In the first week of November, on the outskirts of Ordzhonikidze, the 13th Panzer Division's spearhead was snipped off and the panzer troops had to fall back. The offensive into Russia was over.
Stalingrad: Winter 1942
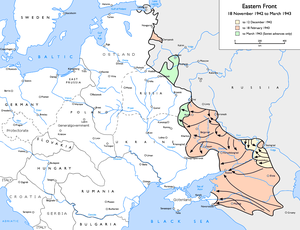
While the German 6th Army and 4th Panzer Army had been fighting their way into Stalingrad, Soviet armies had congregated on either side of the city, specifically into the Don bridgeheads that the Romanians had been unable to reduce, and it was from these that they struck on 19 November 1942. In Operation Uranus, two Soviet fronts punched through the Romanians and converged at Kalach on 23 November, trapping 300,000 Axis troops behind them. A simultaneous offensive on the Rzhev sector known as Operation Mars was supposed to advance to Smolensk, but was a failure, with German tactical flair winning the day.
The Germans rushed to transfer troops to Russia for a desperate attempt to relieve Stalingrad, but the offensive could not get going until 12 December, by which time the 6th Army in Stalingrad was starving and too weak to break out towards it. Operation Winter Storm, with three transferred panzer divisions, got going briskly from Kotelnikovo towards the Aksai river but became bogged down 65 km (40 miles) short of its goal. To divert the rescue attempt the Soviets decided to smash the Italians and come down behind the relief attempt if they could, that operation starting on 16 December. What it did accomplish was to destroy many of the aircraft that had been transporting relief supplies to Stalingrad. The fairly limited scope of the Soviet offensive, although still eventually targeted on Rostov, also allowed Hitler time to see sense and pull Army Group A out of the Caucasus and back over the Don.
On 31 January 1943, the 90,000 survivors of the 300,000-man 6th Army surrendered. By that time the Hungarian 2nd Army had also been wiped out. The Soviets advanced from the Don 500 km (300 miles) to the west of Stalingrad, marching through Kursk (retaken on 8 February 1943) and Kharkov (retaken 16 February 1943). In order to save the position in the south, the Germans decided to abandon the Rzhev salient in February, freeing enough troops to make a successful riposte in eastern Ukraine. Manstein's counteroffensive, strengthened by a specially trained SS panzer corps equipped with Tiger tanks, opened on 20 February 1943, and fought its way from Poltava back into Kharkov in the third week of March, upon which the spring thaw intervened. This had left a glaring bulge in the front centered on Kursk.
Kursk: Summer 1943
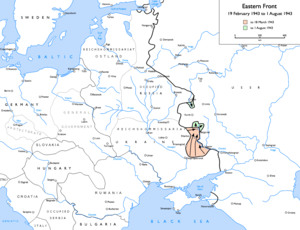
Skabelon:Main article After the failure of the attempt to capture Stalingrad, Hitler had deferred planning authority for the upcoming campaign season to the German Army High Command and reinstated Guderian to a prominent role, this time as Inspector of Panzer Troops. Debate among the General Staff was polarised, with even Hitler nervous about any attempt to pinch off the Kursk salient. He knew that in the intervening six months the Soviet position at Kursk had been reinforced heavily with anti-tank guns, tank traps, landmines, barbed wire, trenches, pillboxes, artillery and mortars. However, if one last great blitzkrieg offensive could be mounted, just maybe the Soviets would ease off and attention could then be turned to the Allied threat to the Western Front. The advance would be executed from the Orel salient to the north of Kursk and from Belgorod to the south. Both wings would converge on the area east of Kursk, and by that means restore the lines of Army Group South to the exact points that it held over the winter of 1941–1942.
Although the Germans knew that the Red Army's reserves of manpower had been bled dry in the summer of 1941 and 1942, the Soviets were still re-equipping, simply by drafting the men from the regions liberated.
Under pressure from his generals, Hitler bit the bullet and agreed to the attack on Kursk, little realising that the Abwehr's intelligence on the Soviet position there had been undermined by a concerted Stavka misinformation and counter-intelligence campaign mounted by the Lucy spy ring in Switzerland. When the Germans began the operation, it was after months of delays waiting for new tanks and equipment, by which time the Soviets had reinforced the Kursk salient with more anti-tank firepower than had ever been assembled in one place before or since.
In the north, the entire 9th Army had been redeployed from the Rzhev salient into the Orel salient and was to advance from Maloarkhangelsk to Kursk. But its forces could not even get past the first objective at Olkhovatka, just 8 km (5 miles) into the advance. The 9th Army blunted its spearhead against the Soviet minefields, frustratingly so considering that the high ground there was the only natural barrier between them and flat tank country all the way to Kursk. The direction of advance was then switched to Ponyri, to the west of Olkhovatka, but the 9th Army could not break through here either and went over to the defensive. The Soviets simply soaked up the German punishment and then struck back. On 12 July the Red Army battled through the demarcation line between the 211th and 293rd divisions on the Zhizdra River and steamed towards Karachev, right behind them and behind Orel.
The southern offensive, spearheaded by 4.Panzer-Armee, led by Gen. Col. Hoth, with three Tank Corps made more headway. Advancing on either side of the upper Donets on a narrow corridor, the SS Panzer Corps and the Großdeutschland Panzergrenadier divisions battled their way through minefields and over comparatively high ground towards Oboyan. Stiff resistance caused a change of direction from east to west of the front, but the tanks got 25 km (15 miles) before encountering the reserves of the Soviet 5th Guards Tank Army outside Prokhorovka. Battle was joined on 12 July, with about one thousand tanks doing battle. After the war, the battle near Prochorovka was idealized by the Soviet historians as the biggest tank battle of all time. The meeting engagement at Prochorovka was a Soviet defensive success, albeit at heavy cost. The Soviet 5th Guards Tank Army, with about 800 light and medium tanks, attacked elements of the II SS Panzer Corps. Tank losses on both sides have been the source of controversy ever since. Although the 5th Guards Tank Army did not attain their terrain objectives, the German advance was halted.
At the end of the day both sides had fought each other to a standstill, but regardless of the standstill in the north Manstein intended to continue the attack with the 4th Panzer Army. But the Soviets could absorb the attack, and German strategic advance in Operation Citadel had been halted. Under the impression of the successful counter-attack operations in the south the Red Army started the strong offensive operation in the northern Orel salient and achieved a breakthrough on the flank of the German 9th Army. Also worried by the Allies' landing in Sicily on 10 July, Hitler made the decision to halve the offensive even as the German 9th Army was rapidly giving ground in the north. The Germans' final strategic offensive in the Soviet Union ended with their defense against a major Soviet counteroffensive that lasted into August. A detailed analysis of this campaign is available in the Battle of Kursk article.
The Kursk offensive was the last on the scale of 1940 and 1941 the Wehrmacht was able to launch, and subsequent offensives would represent only a shadow of previous German offensive might. Following the defeat, Hitler would not trust his generals to the same extent again, and the quality of German strategic decision fell correspondingly. The Battle of Kursk cost Hitler over 500,000 troops and 1,000 tanks, forever hampering future war efforts on the Eastern Front.
Autumn and Winter 1943
The Soviet juggernaut got rolling in earnest with the advance into the Germans' Orel salient. The diversion of Hitler's favourite Grossdeutschland Division from Belgorod to Karachev could not stop it, and a strategic decision was made to abandon Orel (retaken by the Red Army on 5 August 1943) and fall back to the Hagen line in front of Bryansk. To the south, the Soviets blasted through Army Group South's Belgorod positions and headed for Kharkov once again. Though intense battles of movement throughout late July and into August 1943 saw the Tigers blunting Soviet tanks on one axis, they were soon outflanked on another line to the west as the Soviets advanced down the Psel, and Kharkov had to be evacuated for the final time on 22 August.
The German forces on the Mius, now constituting the 1st Panzer Army and a reconstituted 6th Army, were by August too weak to sustain a Soviet attack on their own front, and when the Soviets hit them they had to fall back all the way through the Donbass industrial region to the Dnieper, losing the industrial resources and half the farmland that Germany had invaded the Soviet Union to exploit. At this time Hitler agreed to a general withdrawal to the Dnieper line, along which was meant to be the Ostwall, a line of defence similar to the Westwall of fortifications along the German frontier in the west. Trouble was, it hadn't been built yet, and by the time Army Group South had evacuated eastern Ukraine and begun withdrawing across the Dnieper during September, the Soviets were hard behind them. Tenaciously, small units paddled their way across the 3-km (2-mile) wide river and established bridgeheads. A second attempt by the Soviets to gain land using parachutists, mounted at Kanev on 24 September, proved as luckless as at Dorogobuzh eighteen months previously, and the paratroopers were soon repelled — but not before still more Red Army troops had used the cover they provided to get themselves over the Dnieper and securely dug in. As September proceeded into October, the Germans found the Dnieper line impossible to hold as the Soviet bridgeheads grew and grew, and important Dnieper towns started to fall, with Zaporozhye the first to go, followed by Dnepropetrovsk. Finally, early in November the Soviets broke out of their bridgeheads on either side of Kiev and captured the Ukrainian capital, at that time the third largest city in the Soviet Union.
Eighty miles west of Kiev, the 4th Panzer Army, still convinced that the Red Army was a spent force, was able to mount a successful riposte at Zhitomir during the middle of November, blunting the Soviet bridgehead via a daring outflanking strike mounted by the SS Panzer Corps along the river Teterev. This battle also enabled Army Group South to recapture Korosten and gain some time to rest; however, on Christmas Eve the retreat began anew when the First Ukrainian Front (renamed from Voronezh Front) struck them in the same place. The Soviet advance continued along the railway line until the 1939 Polish-Soviet border was reached on 3 January 1944. To the south, Second Ukrainian Front (ex Steppe Front) had crossed the Dnieper at Kremenchug and continued westwards. In the second week of January 1944 they swung north, meeting Vatutin's tank forces who had swung south from their penetration into Poland and surrounding ten German divisions at Korsun-Shevenkovsky, west of Cherkassy. Hitler's insistence on holding the Dnieper line, even when facing the prospect of catastrophic defeat, was compounded by his conviction that the Cherkassy pocket could break out and even advance to Kiev, but Manstein was more concerned about being able to advance to the edge of the pocket and then implore the surrounded forces to break out. By 16 February the first stage was complete, with panzers separated from the contracting Cherkassy pocket only by the swollen Gniloy Tikich river. Under shellfire and pursued by Soviet tanks, the surrounded German troops, among whom were the SS Division Wiking, fought their way across the river to safety, losing half their number and all their equipment. Surely the Soviets would not attack again, with the spring approaching - but in March 3 the Soviet Ukrainian Front went over to the offensive. Having already isolated the Crimea by severing the neck of the Perekop isthmus, Malinovsky's forces advanced across the mud to the Romanian border, not stopping on the river Prut.
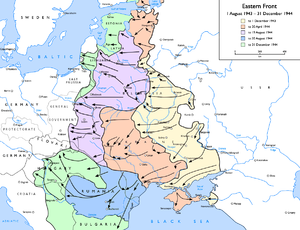
One final move in the south completed the 1943-44 campaigning season, which had wrapped up an advance of over 500 miles. In March, 20 German divisions of Generaloberst Hans-Valentin Hube's 1st Panzer Army were encircled in what was to be known as Hube's Pocket near Kamenets-Podolskiy. After two weeks hard fighting, the 1st Panzer managed to escape the pocket, suffering only light to moderate casualties. At this point, Hitler sacked several prominent generals, Manstein included. April saw the liberation of Odessa in April 1944, followed by 4th Ukrainian Front's campaign to liberate the Crimea, which culminated with the liberation of Sevastopol on 10 May.
Along Army Group Centre's front, August 1943 saw this force pushed back from the Hagen line slowly, ceding comparatively little territory, but the loss of Bryansk and more importantly, Smolensk, on 25 September cost the Wehrmacht the keystone of the entire German defensive system. The 4th and 9th armies and 3rd Panzer Army still held their own east of the upper Dnieper, stifling Soviet attempts to reach Vitebsk. On Army Group North's front, there was barely any fighting at all until January 1944, when out of nowhere Volkhov and Second Baltic Fronts struck. In a lightning campaign, Leningrad and Novgorod were liberated. By February the Red Army had reached the borders of Estonia after a 75 mile advance. The Baltic Sea seemed the quickest way to Stalin to take the battles to the German ground in East Prussia and seizing control of Finland.[17] The Soviet offensive towards the Baltic port of Tallinn was stopped in February 1944. The German forces included Estonian conscripts and volunteers, defending the re-establishment of Estonian independence.[18][19]
Summer 1944
Wehrmacht planning was convinced that the Soviets would attack again in the south, where the front was fifty miles from Lvov and offered the most direct route to Berlin. Accordingly they stripped troops from Army Group Centre, whose front still protruded deep into the Soviet Union. The Belorussian Offensive (codenamed Operation Bagration) started on June 22 1944, was a massive Soviet attack, consisting of four Soviet army groups totaling over 120 divisions that smashed into a thinly-held German line. They focused their massive attacks on Army Group Centre, not Army Group South as the Germans had originally expected. The Germans had transferred some units to France to counter the invasion of Normandy two weeks before. The Red Army achieved a ratio of ten to one in tanks and seven to one in aircraft over the enemy. At the points of attack, the numerical and quality advantages of the Soviets were overwhelming. More than 2.3 million Soviet troops went into action against the German Army Group Centre, which could boast a strength of less than 800,000 men. The Germans crumbled. The capital of Belarus, Minsk, was taken on July 3, trapping 50,000 Germans. Ten days later the Red Army reached the prewar Polish border. Bagration was by any measure one of the largest single operations of the war. By the end of August 1944 it had cost the Red Army ~170,000 dead and missing (765,815 totally, including wounded and sick plus 5073 Poles),[20] as well as 2,957 tanks and assault guns. In the operations, the Germans lost approximately 670,000 dead, missing, wounded and sick, out of whom 160,000 were captured, as well as 2,000 tanks and 57,000 other vehicles.
The neighbouring Lvov-Sandomierz operation was launched on 17 July 1944, rapidly routing the German forces in the western Ukraine. The Soviet advance in the south continued into Romania and, following a coup against the Axis-allied government of Romania on August 23, the Red Army occupied Bucharest on August 31. In Moscow on September 12, Romania and the Soviet Union signed an armistice on terms Moscow virtually dictated. The Romanian surrender tore a hole in the southern German Eastern Front causing the inevitable loss of the whole of the Balkans.
The rapid progress of Operation Bagration threatened to cut off and isolate the German units of Army Group North bitterly resisting the Soviet advance to the Baltic port of Tallinn and the Soviet re-occupation of Estonia. In a ferocious attempt in the Sinimäed Hills, Estonia, the Soviet Leningrad Front failed to break through the defence of the smaller well-fortified Army Group Narwa in a terrain not suitable for large scale operations.[21][22]
In Poland, as the Red Army approached, the Polish Home Army (AK) launched Operation Tempest. During the Warsaw Uprising, the Soviet Army halted at the Vistula River, unable or unwilling to come to the aid of the Polish resistance. An attempt by the communist controlled 1st Polish Army to relieve the city was unsupported by the Red Army and was thrown back in September with heavy losses.
In Slovakia, the Slovak National Uprising started as an armed struggle between German Wehrmacht forces and rebel Slovak troops in August to October 1944. It was centered at Banská Bystrica.
Autumn 1944
On 8 September 1944 the Red Army begun an attack on the Dukla Pass on the Slovak-Polish border. Two months later, the Soviets won the battle and entered Slovakia. The toll was high: 85,000 Red Army soldiers lay dead, plus several thousand Germans, Slovaks and Czechs.
Under the pressure of the Soviet Baltic Offensive, the German Army Group North were withdrawn to fight in the sieges of Saaremaa, Courland and Memel.
January-March 1945

Main articles: Vistula-Oder Offensive (January-February) with the follow-up East Pomeranian Offensive and Silesian Offensives (February-April), East Prussian Offensive (January-April), Vienna Offensive (March-April)
The Soviet Union finally entered Warsaw in January 1945, after it was destroyed and abandoned by the Germans. Over three days, on a broad front incorporating four army fronts, the Red Army began an offensive across the Narew River and from Warsaw. The Soviets outnumbered the Germans on average by five~six to one in troops, six to one in artillery, six to one in tanks and four to one in self-propelled artillery. After four days the Red Army broke out and started moving thirty to forty kilometres a day, taking the Baltic states, Danzig, East Prussia, Poznań, and drawing up on a line sixty kilometres east of Berlin along the Oder River. During the full course of the Vistula-Oder operation (23 days), the Red Army forces sustained 194,000 total casualties (killed, wounded, and missing) and lost 1,267 tanks and assault guns.
On 25 January 1945, Hitler renamed three army groups. Army Group North became Army Group Courland; Army Group Centre became Army Group North and Army Group A became Army Group Centre. Army Group North (old Army Group Centre) was driven into an ever smaller pocket around Königsberg in East Prussia.
A limited counter-attack (codenamed Operation Solstice) by the newly created Army Group Vistula, under the command of Reichsführer-SS Heinrich Himmler, had failed by February 24, and the Soviets drove on to Pomerania and cleared the right bank of the Oder River. In the south, three German attempts to relieve the encircled Budapest failed and the city fell on February 13 to the Soviets. Again the Germans counter-attacked, Hitler insisting on the impossible task of regaining the Danube River. By March 16 the attack had failed and the Red Army counterattacked the same day. On March 30 they entered Austria and captured Vienna on April 13.
OKW claim german losses of 377,000 killed, 334, 000 wounded and 292,000 missing, with a total of 1.103,000 men, on the Eastern Front during January and February 1945. [23]
On April 9, 1945, Königsberg finally fell to the Red Army, although the shattered remnants of Army Group North continued to resist on the Heiligenbeil and Danzig beachheads until the end of the war in Europe. The East Prussian operation, though often overshadowed by the Vistula-Oder operation and the later battle for Berlin, was in fact one of the largest and costliest operations fought by the Red army through the war. During the period it lasted (13 January - 25 April), it cost the Red Army 584,788 casualties, and 3,525 tanks and assault guns.
By early April, the Stavka freed up General Konstantin Rokossovsky's 2nd Belorussian Front (2BF) to move west to the east bank of the Oder river. During the first two weeks of April, the Soviets performed their fastest front redeployment of the war. General Georgy Zhukov concentrated his 1st Belorussian Front (1BF), which had been deployed along the Oder river from Frankfurt in the south to the Baltic, into an area in front of the Seelow Heights. The 2BF moved into the positions being vacated by the 1BF north of the Seelow Heights. While this redeployment was in progress gaps were left in the lines and the remnants of the German 2nd Army, which had been bottled up in a pocket near Danzig, managed to escape across the Oder. To the south General Ivan Konev shifted the main weight of the 1st Ukrainian Front (1UF) out of Upper Silesia north-west to the Neisse River.[24] The three Soviet fronts had altogether 2.5 million men (including 78,556 soldiers of the 1st Polish Army); 6,250 tanks; 7,500 aircraft; 41,600 artillery pieces and mortars; 3,255 truck-mounted Katyushas rockets, (nicknamed "Stalin Organs"); and 95,383 motor vehicles, many manufactured in the USA.[24]
End of War: April–May 1945
Main articles: Battle of Berlin, Battle of Halbe, Prague Offensive

All that was left for the Soviets to do was to launch an offensive to capture what was to become East Germany. The Soviet offensive had two objectives. Because of Stalin's suspicions about the intentions of the Western Allies to hand over territory occupied by them in the post-war Soviet zone of occupation, the offensive was to be on a broad front and was to move as rapidly as possible to the west, to meet the Western Allies as far west as possible. But the overriding objective was to capture Berlin. The two were complementary because possession of the zone could not be won quickly unless Berlin was taken. Another consideration was that Berlin itself held strategic assets, including Adolf Hitler and the German atomic bomb program.[25]
The offensive to capture East Germany and Berlin started on April 16 with an assault on the German front lines on the Oder and Neisse rivers. After several days of heavy fighting the Soviet 1BF and 1UF had punched holes through the German front line and were fanning out across East Germany. By the April 24 elements of the 1BF and 1UF had completed the encirclement of Berlin and the Battle of Berlin entered its final stages. On April 25 the 2BF broke through the German 3rd Panzer Army's line south of Stettin. They were now free to move west towards the British 21st Army Group and north towards the Baltic port of Stralsund. The 58th Guards Rifle Division of the 5th Guards Army made contact with the US 69th Infantry Division of the First Army near Torgau, Germany at the Elbe river.[26][27]
On April 30, as the Soviet forces fought their way into the centre of Berlin, Adolf Hitler married Eva Braun and then committed suicide by taking cyanide and shooting himself. Helmuth Weidling, defence commandant of Berlin, surrendered the city to the Soviets on May 2.[28] Altogether, the Berlin operation (16 April - 8 May) cost the Red Army 81,367 casualties (dead, missing, wounded and sick) and 1,997 tanks and assault guns. German losses in this period of the war remain impossible to determine with any reliability.[kilde mangler]
At 22:41 on the morning of May 7, 1945, at the SHAEF headquarters, German Chief-of-Staff General Alfred Jodl signed the unconditional surrender documents for all German forces to the Allies. It included the phrase All forces under German control to cease active operations at 2301 hours Central European time on May 8 1945. The next day shortly before midnight, Field Marshal Wilhelm Keitel repeated the signing in Berlin at Zhukov's headquarters. The war in Europe was over.[29]
In the Soviet Union the end of the war is considered to be May 9, when the surrender took effect Moscow time. This date is celebrated as a national holiday - Victory Day - in Russia (as part of a two-day May 8-9 holiday) and some other post-Soviet countries. The ceremonial Victory parade was held in Moscow on June 24.
German Army Group Centre initially refused to surrender and continued to fight in Czechoslovakia until about May 11.[30]
A small German garrison on the island of Bornholm (Denmark) refused to surrender until after being bombed and invaded by the Soviets. The island was returned to the Danish government four months later.
Soviet Far East: August 1945
The Manchurian Strategic Offensive Operation began on August 8, 1945, with the Soviet invasion of the Japanese puppet states of Manchukuo and neighbouring Mengjiang; the greater offensive would eventually include northern Korea, southern Sakhalin, and the Kuril Islands. It marked the initial and only military action of the Soviet Union against the Empire of Japan; at the Yalta Conference, it had agreed to Allied pleas to terminate the neutrality pact with Japan and enter the Second World War's Pacific theatre within three months after the end of the war in Europe. While not a part of the Eastern Front operations, it is included here because the commanders and much of the forces used by the Red Army, came from the European Theatre of operations and benefited from the experience gained there. In many ways this was a 'perfect' operation, delivered with the skill gained during the bitter fighting with the Wehrmacht and Luftwaffe over four years[31].
Leadership
The Soviet Union and Nazi Germany were ideologically driven states, in which the leader had near-absolute power. The character of the war was thus determined by the leaders and their ideology to a much greater extent than in any other theatre of World War II.
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler exercised a tight control over the war, spending much of his time in his command bunkers (most notably at Rastenburg in East Prussia, at Vinnitsa in Ukraine, and under the garden of the Reich Chancellery in Berlin). At crucial periods in the war he held daily situation conferences, at which he used his remarkable talent for public speaking to overwhelm opposition from his generals and the OKW staff with rhetoric.
In part because of the unexpected success of the Battle of France despite the warnings of the professional military, Hitler believed himself a military genius, with a grasp of the total war effort that eluded his generals. In August 1941 when Walther von Brauchitsch (commander-in-chief of the Wehrmacht) and Fedor von Bock were appealing for an attack on Moscow, Hitler instead ordered the encirclement and capture of Ukraine, in order to acquire the farmland, industry, and natural resources of that country. Some historians believe that this decision was a missed opportunity to win the war.
In the winter of 1941–42 Hitler believed that his obstinate refusal to allow the German armies to retreat had saved Army Group Centre from collapse. He later told Erhard Milch,
- I had to act ruthlessly. I had to send even my closest generals packing, two army generals, for example … I could only tell these gentlemen, "Get yourself back to Germany as rapidly as you can — but leave the army in my charge. And the army is staying at the front."
The success of this hedgehog defence outside Moscow led Hitler to insist on the holding of territory when it made no military sense, and to sack generals who retreated without orders. Officers with initiative were replaced with yes-men or fanatical Nazis. The disastrous encirclements later in the war — at Stalingrad, Korsun and many other places — were the direct result of Hitler's orders. Many divisions became cut off in "fortress" cities, or wasted uselessly in secondary theatres, because Hitler would not sanction retreat or abandon voluntarily any of his conquests.
Frustration at Hitler's leadership of the war was one of the factors in the attempted coup d'etat of 1944, but after the failure of the July 20 Plot Hitler considered the army and its officer corps suspect and came to rely on the Schutzstaffel and Nazi party members to prosecute the war. His many disastrous appointments included that of Heinrich Himmler to command Army Group Vistula in the defence of Berlin in 1945 — Himmler suffered a mental breakdown under the stress of the command and was quickly replaced by Gotthard Heinrici.
Hitler's direction of the war was disastrous for the German Army, though the skill, loyalty, professionalism and endurance of officers and soldiers enabled him to keep Germany fighting to the end. F. W. Winterbotham wrote of Hitler's signal to Gerd von Rundstedt to continue the attack to the west during the Battle of the Bulge:
- "From experience we had learned that when Hitler started refusing to do what the generals recommended, things started to go wrong, and this was to be no exception."
Joseph Stalin
Joseph Stalin bore the greatest responsibility for the disasters at the beginning of the war, but can be equally praised for the subsequent success of the Soviet Army, which would have been impossible without the unprecedentedly rapid industrialization of the Soviet Union, which was the first priority of Stalin's internal policy throughout the 1930s.
Stalin's Great Purge of the Red Army in the late 1930s consisted of the legal prosecution of many of the senior command, many of whom were convicted and sentenced to death or imprisonment. The executed included Mikhail Tukhachevsky, the brilliant proponent of armoured blitzkrieg. Stalin promoted some obscurantists like Grigory Kulik (who opposed the mechanization of the army and the production of tanks), but on the other hand the purge of the older commanders who had had their positions since the Russian Civil War, and had experience, but were deemed “politically unreliable”. This opened up those places to the promotion of many younger officers that Stalin and the NKVD thought were in line with Stalinist politics, many of whom proved to be terribly inexperienced, but some were later very successful. Soviet tank output remained the largest in the world. Distrust of the military led, since the foundation of the Red Army in 1918, to a system of "dual command", in which every commander was paired with a political commissar, a member of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union. Larger units had military councils consisting of the commander, commissar and chief of staff, who ensured that the commanding officer was loyal and implemented Party orders.
Following the Soviet occupation of eastern Poland, the Baltic states and Bessarabia in 1939–40, Stalin insisted that every fold of the new territories should be occupied; this move westward left troops far from their depots in salients that left them vulnerable to encirclement. There was an assumption that, in the event of a German invasion, the Red Army would take the strategic offensive and fight the war mostly outside the borders of the Soviet Union; thus few plans were made for strategic defensive operations. However, fortifications were built. As tension heightened in spring 1941, Stalin was desperate not to give Hitler any provocation that could be used as an excuse for an attack; this caused him to refuse to allow the military to go onto the alert even as German troops gathered on the borders and German reconnaissance planes overflew installations. This refusal to take the necessary action was instrumental in the destruction of major portions of the Red Air Force, lined up on its airfields, in the first days of the war.
Stalin's insistence on repeated counterattacks without adequate preparation led to the loss of almost the whole of the Red Army's tank corps in 1941 — many tanks simply ran out of fuel on their way to the battlefield through faulty planning or ignorance of the location of fuel dumps. While some regard this offensive strategy as an argument for Soviet aggressive strategic plans, the offensive operational planning was not, by itself, evidence of any aggressive foreign policy intent.
Unlike Hitler, Stalin was able to learn lessons and improve his conduct of the war. He gradually came to realise the dangers of inadequate preparation and built up a competent command and control organization — the Stavka — under Semyon Timoshenko, Georgy Zhukov and others. Incompetent commanders were gradually but ruthlessly weeded out.
At the crisis of the war, in autumn 1942, Stalin made many concessions to the army: unitary command was restored by removing the Commissars from the chain of command. After the Battle of Stalingrad, shoulderboards were introduced for all ranks; this was a significant symbolic step, since they had been seen as a symbol of the old regime after the Russian Revolution of 1917. Beginning in autumn 1941, units that had proved themselves by superior performance in combat were given the traditional "Guards" title. But these concessions were combined with ruthless discipline: Order No. 227, issued on 28 July 1942, threatened commanders who retreated without orders with punishment by court-martial. Infractions by military and politruks were punished with transferral to penal battalions and penal companies, and the NKVD's barrier troops would shoot soldiers who fled.
As it became clear that the Soviet Union would win the war, Stalin ensured that propaganda always mentioned his leadership of the war; the victorious generals were sidelined and never allowed to develop into political rivals. After the war the Red Army was once again purged (but not as brutally as in the 1930s): many successful officers were demoted to unimportant positions (including Zhukov, Malinovsky and Koniev).
Occupation and repression
The enormous territorial gains of 1941 presented Germany with vast areas to pacify and administer. Some Soviet citizens, especially in the recently occupied territories of Western Ukraine and the Baltic States greeted their conquerors as liberators from the Soviet rule. However, nascent national liberation movements among Ukrainians and Cossacks, and others were viewed by Hitler with suspicion; some, (especially those from the Baltic States) were co-opted into the Axis armies and others brutally suppressed. None of the conquered territories gained any measure of self-rule. Instead, the racist Nazi ideologues saw the future of the East as one of settlement by German colonists, with the natives killed, expelled, or reduced to slave labour (Generalplan Ost).
Regions closer to the front were managed by military powers of the region, in other areas such as Baltic states annexed by USSR in 1940, Reichscommissariats were established. As a rule, the maximum in loot was extracted. In September 1941, Erich Koch was appointed to the Ukrainian Commissariat. His opening speech was clear about German policy: "I am known as a brutal dog … Our job is to suck from Ukraine all the goods we can get hold of ... I am expecting from you the utmost severity towards the native population."
Atrocities against the Jewish population in the conquered areas began almost immediately, with the dispatch of Einsatzgruppen (task groups) to round up Jews and shoot them. Local anti-semites were encouraged to carry out their own pogroms. In July 1941 Erich von dem Bach-Zalewski's SS unit began to carry out more systematic killings, including the massacre of over 30,000 Jews at Babi Yar. By the end of 1941 there were more than 50,000 troops devoted to rounding up and killing Jews. The gradual industrialization of killing led to adoption of the Final Solution and the establishment of the Operation Reinhard extermination camps: the machinery of the Holocaust. In three years of occupation, between one and two million Soviet Jews were killed. Other ethnic groups were targeted for extermination, including the Roma and Sinti; see Porajmos.
The massacres of Jews and other ethnic minorities were only a part of the deaths from the Nazi occupation. Many hundreds of thousands of Soviet civilians were executed, and millions more died from starvation as the Germans requisitioned food for their armies and fodder for their draft horses. As they retreated from Ukraine and Belarus in 1943–44, the German occupiers systematically applied a scorched earth policy, burning towns and cities, destroying infrastructure, and leaving civilians to starve or die of exposure. In many towns, the Germans also fought Soviet forces right within towns and cities with trapped civilians caught in the middle. Estimates of total civilian dead in the Soviet Union in the war range from seven million (Encyclopædia Britannica) to seventeen million (Richard Overy).
The Nazi ideology and the maltreatment of the local population and Soviet POWs encouraged partisans fighting behind the front, motivated even anti-communists or non-Russian nationalists to ally with the Soviets, and greatly delayed the formation of German allied divisions consisting of Soviet POWs (see Vlasov army). These results and missed opportunities contributed to the defeat of the Wehrmacht.

A Russian historian Vadim Erlikman has detailed Soviet losses totaling 26.5 million war related deaths. Military losses of 10.6 million include 7.6 million killed or missing in action and 2.6 million POW dead, plus 400,000 paramilitary and Soviet partisan losses. Civilian deaths totaled 15.9 million, which included 1.5 million from military actions; 7.1 million victims of Nazi genocide and reprisals; 1.8 million deported to Germany for forced labor; and 5.5 million famine and disease deaths. Additional famine deaths, which totaled 1 million during 1946-47, are not included here. These losses are for the entire territory of the USSR including territories annexed in 1939-40.[1]
Belarus lost a quarter of its pre-war population, including practically all its intellectual elite. Following bloody encirclement battles, all of the present-day Belarus territory was occupied by the Germans by the end of August 1941. The Nazis imposed a brutal regime, deporting some 380,000 young people for slave labour, and killing hundreds of thousands of civilians more. More than 600 villages like Khatyn were burned with their entire population.[2] More than 209 cities and towns (out of 270 total) and 9,000 villages were destroyed. Himmler pronounced a plan according to which 3/4 of Belarusian population was designated to "eradication" and 1/4 of racially cleaner population (blue eyes, light hair) would be allowed to serve Germans as slaves.
Some recent reports raise the number of Belarusians who perished in War to "3 million 650 thousand people, unlike the former 2.2 million. That is to say not every fourth inhabitant but almost 40% of the pre-war Belarusian population perished (considering the present-day borders of Belarus)." [3]
Sixty percent of Soviet POWs died during the war. Large numbers of Soviet POWs and forced laborers transported to Germany were on their return to the USSR (in many cases forcefully repatriated by the Western Allies) treated as traitors and deserters and were executed or deported to the Soviet prison camps. The Soviet Union had not signed the Geneva Convention (1929). However, a month after the German invasion in 1941, an offer was made for a reciprocal adherence to the Hague convention. This 'note' was left unanswered by Third Reich officials [32].
The official Polish government report of war losses prepared in 1947 reported 6,028,000 war victims out of a population of 27,007,000 ethnic Poles and Jews; this report excluded ethnic Ukrainian and Belarusian losses.
Industrial output
The Soviet victory owed a great deal to the ability of her war industry to outperform the German economy, despite the enormous loss of population and land. Stalin's five-year plans of the 1930s had resulted in the industrialization of the Urals and central Asia. In 1941, the trains that shipped troops to the front were used to evacuate thousands of factories from Belarus and Ukraine to safe areas far from the front lines.
As the Soviet Union's manpower reserves ran low from 1943 onwards, the great Soviet offensives had to depend more on equipment and less on the expenditure of lives. The increases in production of war materiel were achieved at the expense of civilian living standards — the most thorough application of the principle of total war — and with the help of Lend-Lease supplies from the United Kingdom and the United States. The Germans, on the other hand, could rely on a large slave workforce from the conquered countries and Soviet POWs.
Germany's raw material production was higher than the Soviets' and her labour force was far greater, but the Soviets were more efficient at using what resources they had and chose to build low-cost, low-maintenance vehicles whilst the Germans built high-cost, high-maintenance vehicles.
Germany chose to build very expensive and very complicated vehicles and even though Germany produced many times more raw materials she could not compete with the Soviets on the quantity of military production (in 1943, the Soviet Union manufactured 24,089 tanks to Germany's 19,800). The Soviets incrementally upgraded existing designs, and simplified and refined manufacturing processes to increase production. Meanwhile, German industry was forced to engineer more advanced but complex designs such as the Panther tank, the King Tiger or the Elefant.
| Year | Coal (million tonnes) |
Steel (million tonnes) |
Aluminium (thousand tonnes) |
Oil (million tonnes) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| German | Soviet | German | Soviet | German | Soviet | German | Soviet | Italian | Hungarian | Romanian | Japanese | |
| 1941 | 315.5 | 151.4 | 28.2 | 17.9 | 233.6 | – | 5.7 | 33.0 | 0.12 | 0.4 | 5.5 | - |
| 1942 | 317.9 | 75.5 | 28.7 | 8.1 | 264.0 | 51.7 | 6.6 | 22.0 | 0.01 | 0.7 | 5.7 | 1.8 |
| 1943 | 340.4 | 93.1 | 30.6 | 8.5 | 250.0 | 62.3 | 7.6 | 18.0 | 0.01 | 0.8 | 5.3 | 2.3 |
| 1944 | 347.6 | 121.5 | 25.8 | 10.9 | 245.3 | 82.7 | 5.5 | 18.2 | - | 1 | 3.5 | 1 |
| 1945[34] | – | 149.3 | – | 12.3 | – | 86.3 | 1.3 | 19.4 | - | - | - | 0.1 |
| Year | Tanks and self- propelled guns | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soviet | German | Italian | Hungarian | Japanese | |
| 1941 | 6,590 | 5,200[35] | 595 | - | 595 |
| 1942 | 24,446 | 9,300[35] | 1,252 | 500 | 557 |
| 1943 | 24,089 | 19,800 | 336 | 558 | |
| 1944 | 28,963 | 27,300 | - | 353 | |
| 1945[34] | 15,400 | – | - | - | 137 |
| Year | Aircraft | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soviet | German | Italian | Hungarian | Romanian | Japanese | |
| 1941 | 15,735 | 11,776 | 3,503 | - | 1,000 | 5,088 |
| 1942 | 25,436 | 15,556 | 2,818 | 6 | 8,861 | |
| 1943 | 34,845 | 25,527 | 967 | 267 | 16,693 | |
| 1944 | 40,246 | 39,807 | - | 773 | 28,180 | |
| 1945[34] | 20,052 | 7,544 | - | - | 8,263 | |
| Year | Industrial Labour | Foreign Labour | Total Labour | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soviet | German | Soviet | German | Total Soviet | Total German | |
| 1941 | 11,000,000 | 12,900,000 | - | 3,500,000 | 11,000,000 | 16,400,000 |
| 1942 | 7,200,000 | 11,600,000 | 50,000 | 4,600,000 | 7,250,000 | 16,200,000 |
| 1943 | 7,500,000 | 11,100,000 | 200,000 | 5,700,000 | 7,700,000 | 16,800,000 |
| 1944 | 8,200,000 | 10,400,000 | 800,000 | 7,600,000 | 9,000,000 | 18,000,000 |
| 1945[34] | 9,500,000 | – | 2,900,000 | - | 12,400,000 | - |
It should be noted that the Axis allies Italy, Romania, Hungary and Bulgaria added to the German numbers. Two-thirds of Germany's Iron ore, much needed for her military production, came from Sweden. Soviet production and upkeep was assisted by the Lend-Lease program from the United States and Britain. After the defeat at Stalingrad, Germany geared completely towards a war economy, as expounded in Goebbels' Sportpalast speech, increasing production in subsequent years under Albert Speer's astute direction, despite the intensifying Allied bombing campaign.
Casualties
From 1941 on, Stalin was willing to strike back against the invading Axis forces at all costs and led the war with extreme brutality, including against his own soldiers.[37][38] The Red Army took much higher casualties than any other military force during World War II, in part because of high manpower attrition and inadequate time for training.[39] Faced with badly equipped infantry units barely capable of standing up against machine guns, tanks and artillery, the tactics of Soviet commanders were often based on mass infantry attacks, inflicting heavy losses on their own troops. This tactic was also used for clearing minefields, which were ‘attacked’ by waves of infantry soldiers in order to clear them.[40][41][42][37] In accordance with the orders of Soviet High Command, retreating soldiers or even soldiers who hesitated to advance faced being shot by rearguard SMERSH units: Stalin’s order No 270 of August 16, 1941, states that in case of retreat or surrender, all officers involved were to be shot on the spot and all enlisted men threatened with total annihilation as well as possible reprisals against their families.[38].[43][37]
The fighting involved millions of Axis and Soviet troops along the broadest land front in military history. It was by far the deadliest single theatre of war in World War II, with over 5 million deaths on the Axis Forces; Soviet military deaths were about 10.6 million (out of which 3.3 million Soviets died in German captivity[44]), and estimated civilian deaths range from about 14 to 17 million. Over 11.4 million Soviet civilians, and another estimated 3.5 million civilians from the Annexed territories were killed.[45] Soviet and Russian historiography often uses the so-called irretrievable casualties term. According to the Narkomat of Defence order (№ 023, February 4, 1944), the irretrievable casualties include killed, missed, those who died due to war-time or subsequent wounds, maladies and chilblains and those who were captured. Also, the Nazis exterminated over 1 million Soviet Jews [46] and another 4.2 million Jews from the annexed territories which include over 3 million Polish Jews[46] in the Holocaust.
The genocidal death toll was attributed to several factors, including brutal mistreatment of POWs and captured partisans by both sides, multiple atrocities by the Germans and the Soviets against the civilian population and each other, the wholesale use of weaponry on the battlefield against huge masses of infantry. The multiple battles, and most of all, the use of scorched earth tactics destroyed agricultural land, infrastructure, and whole towns, leaving much of the population homeless and without food.
| Forces fighting with the Axis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Dead | KIA/MIA | POWs taken by the Soviets | POWs that died in Captivity | |
| Greater Germany | 4,300,000 | 4,000,000 | 3,300,000 | 374,000 |
| Soviet residents who joined German army | 215,000+ | 215,000 | 1,000,000 | Unknown |
| Romania | 281,000 | 81,000 | 500,000 | 200,000 |
| Hungary | 300,000 | 100,000 | 500,000 | 200,000 |
| Italy | 82,000 | 32,000 | 70,000 | 50,000 |
| Total | 5,178,000+ | 4,428,000 | 5,450,000 | 824,000 |
| Forces Fighting with the Soviet Union | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Dead | KIA/MIA | POWs taken by the Axis | POWs that died in captivity | |
| Soviet | 10,600,000 | 6,600,000 | 5,200,000 | 3,600,000 |
| Poland | 24,000 | 24,000 | Unknown | Unknown |
| Romania | 17,000 | 17,000 | 80,000 | Unknown |
| Bulgaria | 10,000 | 10,000 | Unknown | Unknown |
| Total | 10,651,000 | 6,651,000 | 5,280,000 | 3,600,000 |
Total Soviet losses includes Deaths Partisans-250,000 and Deaths Militia-150,000
Polish Armed Forces in the East, initially consisting of Poles from Eastern Poland or otherwise in Soviet Union in 1939-1941, began fighting alongside the Red Army in 1943, and grew steadily as more Polish territory was liberated from the Nazis in 1944-1945.
When the Axis countries of Eastern Europe were occupied by the Soviets, they were forced to change sides and declare war on Germany. (see Allied Commissions).
Some of the Soviet citizens would side with the Germans and join Andrey Vlasov's Russian Liberation Army. Most of those who joined were Russian POWs. Most who joined hated communism and actually saw the Nazis as liberators from communism. These men were primarily used in the Eastern Front but some were assigned to guard the beaches of Normandy. The other main group of men joining the German army were citizens of the Baltic countries annexed by the Soviet Union in 1940 or from Western Ukraine. They fought in their own Waffen-SS units.
A comparison of the losses demonstrates the cruel treatment of the Soviet POWs by the Nazis. Most of the Axis POWs were released from captivity after the war, but the fate of the Soviet POWs differed markedly. Nazi troops who captured Red Army soldiers frequently shot them in the field or shipped them to concentration camps and executed them. Hitler's notorious Commissar Order implicated all the German armed forces in the policy of war crimes.
See also
- Historiography of World War II
- Timeline of the Eastern Front of World War II
- List of military operations on the Eastern Front of World War II
- Operation Silberfuchs – Axis attack on the Soviet Arctic
- Manchurian Strategic Offensive Operation – the Soviet campaign against Japan in Manchuria, Inner Mongolia, Korea, Sakhalin and the Kurile Islands
- Captured German equipment in Soviet use in Eastern front
- Voenno-vozdushniye Sily – Soviet Air Force in World War II
- Morskaya Aviatsiya – Soviet Naval Air Service in World War II
- Women in the Russian and Soviet military
- Occupation of Belarus by Nazi Germany
- Italian war in Soviet Union, 1941-1943
- Pobediteli – Russian project celebrating the 60th anniversary of World War II
- The Battle of Russia – film from the Why We Fight propaganda film series
Notes
- ^ Sovjetunionen rekrutterede også nogle udenlandske enheder (Tjekkoslovakiske og Rumænske). Sovjetunionen fik også hjælp fra USA og Storbritannien. Hertil kom i mindre omfang støtte fra Polen, Rumænien (fra 1944), Bulgarien (fra 1944) og Tjekkoslovakiet
- ^ Germany's allies, in total, provided a significant number of troops and material to the front. There were also numerous foreign units recruited by Germany, notably the Russian Liberation Army and the Spanish Blue Division.
- ^ (tysk) Die Ostfront 1941-1945
- ^ (tysk) Der Rußlandfeldzug; (tysk) 2. Weltkrieg
- ^
Heinrich Himmler. "Speech of the Reichsfuehrer-SS at the meeting of SS Major-Generals at Posen October 4th, 1943". Source: Nazi Conspiracy and Aggression, Vol. IV. USGPO, Washington, 1946, pp.616-634. Stuart Stein , University of the West of England.
Whether nations live in prosperity or starve to death . . . interests me only in so far as we need them as slaves for our Kultur. . .
- ^
revisions to translation by Dan Rogers. "The Wannsee Conference Protocol". source: John Mendelsohn, ed., _The Holocaust: Selected Documents in Eighteen Volumes._ Vol. 11: The Wannsee Protocol. Literature of the Holocaust, university of pennsylvania. Hentet 2009 1 5.
{{cite web}}: Tjek datoværdier i:|accessdate=(hjælp) - ^ Speer, Albert. Inside the Third Reich. p. 238
- ^ Remembering a Red Flag Day - TIME
- ^ The New York Times, February 9, 1946, Volume 95, Number 32158.
- ^ Chris Bellamy (2007) Absolute War: Soviet Russia in the Second World War. London: Macmillan: 1-2
- ^ [Hardesty, Von. Red Phoenix: The Rise of Soviet Air Power 1941-1945. p. 16, Smithsonian Institution Press. ISBN 1-56098-071-0]
- ^ a b Zhukov, Georgy (1972). Vospominaniya i razmyshleniya. Moscow: Agenstvo pechati Novosti.
{{cite book}}: Cite har en ukendt tom parameter:|coauthors=(hjælp) - ^ Zhilin, P.A. (ed.) (1973). Velikaya Otechestvennaya voyna. Moscow: Izdatelstvo politicheskoi literatury.
{{cite book}}:|first=har et generisk navn (hjælp); Cite har en ukendt tom parameter:|coauthors=(hjælp) - ^ Robert Gellately. Lenin, Stalin, and Hitler: The Age of Social Catastrophe. Knopf, 2007 ISBN 1400040051 p. 391
- ^ (polsk) Encyklopedia PWN, Zbrodnie Sowickie W Polsce
- ^ Louis Rotundo. The Creation of Soviet Reserves and the 1941 Campaign. Military Affairs, Vol. 50, No. 1 (Jan., 1986), pp. 21-28.
- ^ David M. Glantz (2002). The Battle for Leningrad: 1941-1944. Lawrence: University Press of Kansas.
- ^ Estonia. Sept.21 Bulletin of International News by Royal Institute of International Affairs Information Dept.
- ^ "The Otto Tief government and the fall of Tallinn". Estonian Ministry of Foreign Affairs. 2006.
- ^ G. I. Krivosheev. Soviet Casualties and Combat Losses. Greenhill 1997 ISBN 1-85367-280-7
- ^ Estonian State Commission on Examination of Policies of Repression (2005). The White Book: Losses inflicted on the Estonian nation by occupation regimes. 1940 – 1991 (PDF). Estonian Encyclopedia Publishers.
- ^ Toomas Hiio (1999). Combat in Estonia in 1944. In: Toomas Hiio, Meelis Maripuu, Indrek Paavle (Eds.). Estonia 1940–1945: Reports of the Estonian International Commission for the Investigation of Crimes Against Humanity. Tallinn.
- ^ Hastings, Max, Armageddon: The Battle for Germany 1944-1945, Vintage Books USA
- ^ a b Ziemke, Berlin, see References page 71
- ^ Beevor, Berlin, see References Page 138
- ^ Beevor, Berlin, see References pp. 217-233
- ^ Ziemke , Berlin, see References page 81-111
- ^ Beevor, Berlin, see References pp. 259-357, 380-381
- ^ Ziemke, occupation, References CHAPTER XV:The Victory Sealed Page 258 last paragraph
- ^ Ziemke, Berlin, References p. 134
- ^ Raymond L. Garthoff. The Soviet Manchurian Campaign, August 1945. Military Affairs, Vol. 33, No. 2 (Oct., 1969), pp. 312-336
- ^ Beevor, Stalingrad. Penguin 2001 ISBN 0141001313 p60
- ^ a b c Richard Overy, Russia's War, p. 155 and Campaigns of World War II Day By Day, by Chris Bishop and Chris McNab, pp. 244-52.
- ^ a b c d Soviet numbers for 1945 are for the whole of 1945 even after the war was over.
- ^ a b German figures for 1941 and 1942 include tanks only. (Self-propelled guns cost 2/3 of a tank (mainly because they have no turret) and were more appropriate in a defensive role. The Germans therefore favored their production in the second half of the war.)
- ^ The Dictators: Hitler's Germany, Stalin's Russia by Richard Overy p. 498.
- ^ a b c Catherine Merridale, Ivan's War, the Red Army 1939-1945, London: Faber and Faber, 2005, ISBN 0-5712-1808-3
- ^ a b Not-So-Friendly Fire, Queen’s University, Canada
- ^ CSI Report No. 11: Soviet Defensive Tactics at Kursk
- ^ David Glantz, Barbarossa: Hitler's Invasion of Russia 1941 (2001) ISBN 0-7524-1979-X
- ^ David Glantz, Stumbling Colossus: The Red Army on the Eve of World War (1998) ISBN 0-7006-0879-6
- ^ Review of "Stumbling Colossus"
- ^ Order No 270 in Russian language on hrono.ru
- ^ Richard Overy, The Dictators
- ^ G. I. Krivosheev. Soviet Casualties and Combat Losses. Greenhill 1997 ISBN 1-85367-280-7
- ^ a b Martin Gilbert. Atlas of the Holocaust 1988 ISBN 0-688-12364-3
- ^ Rűdiger Overmans, Deutsche militärische Verluste im Zweiten Weltkrieg. Oldenbourg 2000. ISBN 3-486-56531-1, Richard Overy The Dictators: Hitler's Germany and Stalin's Russia (2004), ISBN 0-7139-9309-X
- ^ Vadim Erlikman, Poteri narodonaseleniia v XX veke: spravochnik. Moscow 2004. ISBN 5-93165-107-1; Mark Axworthy, Third Axis Fourth Ally. Arms and Armour 1995, p. 216. ISBN 1-85409-267-7
References
- Beevor, Antony. Berlin: The Downfall 1945, Penguin Books, 2002, ISBN 0-670-88695-5
- Ziemke, Earl F. Battle For Berlin: End Of The Third Reich, NY:Ballantine Books, London:Macdomald & Co, 1969.
- Ziemke, Earl F. "The U.S. Army in the occupation of Germany 1944-1946" Center of Military History, United States Army, Washington, D. C., 1990, Library of Congress Catalog Card Number 75-619027
Bibliography
- Anderson, Dunkan, et al. The Eastern Front: Barbarossa, Stalingrad, Kursk and Berlin (Campaigns of World War II). London: Amber Books Ltd., 2001. ISBN 0-7603-0923-X.
- Beevor, Antony, and Artemis Cooper. Stalingrad: The Fateful Siege: 1942-1943. New York: Penguin Books Ltd., 1998. ISBN 0140284583.
- Beevor, Antony. Berlin: The Downfall 1945. New York: Penguin Books Ltd., 2004. ISBN 0141017473.
- Erickson, John. The Road to Stalingrad. New York: Orion Publishing Group, Ltd., 2007. ISBN 0304365416.
- Erickson, John. The Road to Berlin. New York: Orion Publishing Group, Ltd., 2007. ISBN 978-0304365401.
- Erickson, John, and David Dilks. Barbarossa, the Axis and the Allies. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press, 1995. ISBN 0748605045.
- Glantz, David, and Jonathan M. House. When Titans Clashed: How the Red Army stopped Hitler. Lawrence, Kansas: University Press of Kansas, Reprint edition, 1998. ISBN 0700608990.
- Glantz, David, The Soviet‐German War 1941–45: Myths and Realities: A Survey Essay.
- Guderian, Heinz. Panzer Leader, Da Capo Press Reissue edition. New York: Da Capo Press, 2001. ISBN 0-306-81101-4.
- Hastings, Max. Armageddon: The Battle for Germany, 1944-1945, Vintage Books USA, 2005. ISBN 0375714227
- Irving, David. Hitler's War, Reissue edition. Avon Books, 1990. ISBN 0380758067.
- Liddell Hart, B.H. History of the Second World War. United States of America: De Capo Press, 1999. ISBN 0306809125.
- Lubbeck, William and David B. Hurt. At Leningrad's Gates: The Story of a Soldier with Army Group North, Philadelphia: Casemate, 2006. ISBN 1-932033-55-6.
- Müller, Rolf-Dieter and Gerd R. Ueberschär. Hitler's War in the East, 1941-1945: A Critical Assessment. Berghahn Books, 1997. ISBN 1-57181-068-4.
- Overy, Richard. Russia's War: A History of the Soviet Effort: 1941–1945, New Edition. New York: Penguin Books Ltd., 1998. ISBN 0140271694.
- Seaton, Albert. The Russo-German War, 1941–1945, Reprint edition. Presidio Press, 1993. ISBN 0891414916.
- Winterbotham, F.W. The Ultra Secret, New Edition. Orion Publishing Group Ltd., 2000. ISBN 0752837516.
External links
- Prof Richard Overy writes a summary about the eastern front for the BBC
- Rarities of the USSR photochronicles. Great Patriotic War 1941-1945 Borodulin Collection. Excellent set of war photos
- Russian veterans of World War II memories(In English and Russian)
- OnWar maps of the Eastern Front
- Memories of Leutnant d.R. Wilhelm Radkovsky 1940-1945 Experiences as a German soldier on the Eastern and Western Front
- Pobediteli: Eastern Front flash animation (photos, video, interviews, memorials. Written from a Russian perspective)
- Feldgrau.com The German Armed Forces 1919-1945
- Information about the Eastern front up to September 1943
- RKKA in World War II
- 27 Million
- Pictures of German Occupation in the USSR
- Small Unit Actions During German Campaign in Russia German and Soviet tactics explained, written by former German commanders in the East
- Armchair General maps, year by year
Østfronten er navnet på den række af slag under 2. verdenskrig, som blev ført på den tyske østfront. Ordet betegner derfor på én gang den øjeblikkelige frontlinje på en given dato og helheden af de kampe, der blev indledt ved Tysklands angreb på Sovjetunionen.
Operation "Barbarossa"

Den 22. juni 1941 igangsatte tyskerne en overraskelsesinvasion af Sovjetunionen under betegnelsen operation Barbarossa. De første uger af invasionen var katastrofale for den sovjetiske hær på trods af, at Stalin flere gange var blevet advaret om invasionen, dels fra hans egne efterretninger og dels fra englænderne, der havde data af høj kvalitet fra Enigma. Store hærenheder blev omringet og overgav sig, og luftvåbnet blev nærmest udslettet på jorden. Det var dog ikke alene tyske hærenheder, der udgjorde invasionsstyrken. Italienske, ungarske og rumænske tropper var også en del af felttoget.
Situationen i Finland var meget speciel. Finland erklærede sig først neutral, men havde både tyske og sovjetiske tropper på sit område. Finland var velforberedt på en krig på tysk side, da Sovjetunionen angreb det den 25. juni. Den følgende konflikt 1941-1944 har fået navnet fortsættelseskrigen med henvisning til, at den var en fortsættelse af Vinterkrigen.
Operation Barbarossa havde en række svage punkter. Alvorligst var den logistiske situation. I sidste ende var det logistikken, som var afgørende for den tyske hærs muligheder. De enorme distancer i Sovjetunionen indebar, at tyskerne ikke kunne avancere længere, end deres forsyningslinjer tillod. Da det tyske angreb stoppede foran Moskva den 5. december 1941, var det umuligt at drive tropperne længere fremad. Der var simpelthen ikke forsyninger nok, som nåede frem til fronten, til at et ordentligt forsvar kunne organiseres for slet ikke at tale om offensive operationer. Tidsplanen for det tyske angreb byggede på, at den sovjetiske hær ville kollapse, før den russiske vinter satte ind. At dette ikke skete, påvirkede i høj grad de tyske planer. Fedtet i lejerne på de tyske kampvogne frøs, og tyskerne måtte tage vintertøj fra døde russiske soldater for at overleve. Hvis tyskerne havde omringet Moskva, havde russerne måske bedt om våbenstilstand, da Moskva var knudepunkt for alle de sovjetiske jernbaner, og landet havde ikke tid eller lastbiler nok til at forbinde jernbanerne bag en front øst for Moskva.
Under deres lange tilbagetrækning anvendte de russiske styrker den brændte jords taktik. De brændte afgrøder og ødelagde bygninger og anlæg, efterhånden som de trak sig tilbage for de fremadstormende tyske tropper. Dette forøgede drastisk de tyske forsyningsproblemer, samtidig med at tabene på grund af den frygtede russiske kulde og russiske modangreb steg kraftigt. Flere hundrede tusinde soldater døde på grund af disse faktorer.
På trods af problemer med yderligere at fremskynde deres fremrykning havde tyskerne på dette tidspunkt erobret et enormt område. Tilbageerobringen af dette område kom til at koste Sovjetunionen dyrt og varede indtil sent i 1944.
Belejringen af Leningrad
Tyskernes store erobringer bragte dem også tæt på Leningrad (nu Sankt Petersborg), og udløste hermed en af krigens tragedier – belejringen af Leningrad. Finske tropper stødte frem mod byen fra nord og den tyske værnemagt fra syd. Den finske øverstbefalende, Carl Gustaf Mannerheim, var stoppet ved floden Svir og afstod fra at angribe byen. Hitler derimod beordrede, at byen skulle "fjernes fra jordens overflade", sammen med hele sin befolkning. Byen blev derfor ikke stormet. Den tyske hær omringede i stedet byen næsten fuldstændigt for at sulte dens befolkning ihjel, samtidig med at bombefly og artilleri sendte en regn af bomber og granater over byen. Cirka en million civile døde under belejringen af Leningrad – 800.000 af sult. Belejringen varede 900 dage, og da den var mest omfattende, var den eneste vej ind og ud af byen over den tilfrosne sø Ladoga, midt imellem de tyske og finske linjer. Man anlagde endog en jernbane på isen. På et tidspunkt brækkede isen, og et langt stykke jernbaneskinner forsvandt i dybet. Ingen anden materiel skade.

(siddende): Premierminister Winston Churchill (UK), præsident Franklin D. Roosevelt (US) og formand Josef Stalin (USSR). Stående længst til venstre ses den sovjetiske udenrigsminister Molotov
Kampen om Stalingrad
Da vinteren 1941-42 var overstået, begyndte den tyske hær at forberede yderligere offensive aktioner. Frem for en offensiv mod Moskva blev prioriteringen ændret til retning mod Stalingrad (nu Volgograd) ved floden Volga og mod Kaukasus. Stalingrad (vest for floden) blev erobret med undtagelse af nogle små modstandslommer, men kampagnen tog en katastrofal vending for de tyske styrker.
Ubeslutsomhed hos Adolf Hitler, uenighed blandt højtstående tyske officerer og udstrakte forsyningslinjer kombineret med længerevarende bykampe i Stalingrad gjorde den tyske stilling udsat. I et forsøg på at fremskynde byens fald blev store tyske inklusive reserver og pansertropper, der fungerede som infanteri, indsat i selve byen. De meget lange flanker ved Don-floden blev herefter delvist forsvaret af forholdsvis svage rumænske, italienske og ungarske styrker. Efter en sovjetisk modoffensiv (Operation Uranus) i november 1942, blev den tyske 6. armé sammen med det 4. panserkorps afskåret. Sult, mangel på mad og ammunition gjorde at "kedlen" gradvis blev mindre og mindre. Hitler beordrede, at ingen tyske tropper måtte overgive sig: De skulle kæmpe til sidste mand og sidste patron, og han udnævnte symbolsk general Paulus til generalfeltmarskal, da ingen tysk soldat med den rang tidligere havde overgivet sig. Dette skete alligevel i begyndelsen af februar 1943. Begge sider led store tab i slaget om Stalingrad, som blev historiens hidtil største og mest blodige slag. Det anslås, at 2 millioner mennesker døde i slaget om Stalingrad, herunder 500.000 civile.
Kampvognsslaget ved Kursk
Efter Stalingrad blev det tyske initiativ svagere. Sovjet formåede dog ikke at gribe dette fuldt ud, idet en offensiv, Operation Zitadelle, i sommeren 1943 under von Manstein stoppede det sovjetiske angreb. Slaget ved Kursk blev det største kampvognsslag, historien endnu havde set, og den blev tyskernes sidste større offensiv på østfronten. Gode efterretninger havde forberedt Sovjetunionen på det tyske modangreb, og man havde forberedt massive forsvarslinjer omkring Kursk. Russerne var herefter i offensiven, indtil Berlin blev erobret i maj 1945, og krigen sluttede.
Konsekvenser
Sovjetunionen kom til at bære den største del af omkostningerne ved 2. verdenskrig. Den anden front i Europa, der skulle aflaste østfronten, blev først realiseret på D-dag (bortset fra invasionen af Italien). Landet havde derfor flere ofre end samtlige øvrige lande tilsammen: cirka 27 millioner døde, heraf mere end 13 millioner civile. Mange civile blev myrdet i erobrede byer af tyskerne, der dels anså befolkningen for at være undermennesker, dels havde planer om at genbefolke landet med tyskere.
Sovjetunionen kæmpede dog ikke alene. Britiske og amerikanske forsyningskonvojer sejlede under stor risiko forsyninger til landet. Tyske styrker blev anvendt til at beskytte kystlinjer mod angreb, som aldrig blev iværksat og til at bemande antiluftskyts over hele Europa. Sovjetunionen tog heller ikke aktivt del i søslagene, bombeoffensiverne og sejren over Japan. Den 8. august 1945 angreb Sovjetunionen dog med tre armeer, som led i Jalta-aftalen, de japanske styrker i Manchuriet, og på to uger nedkæmpede Den Røde Hær en million japanske tropper.
Skabelon:Link FA Skabelon:Link FA Skabelon:Link FA Skabelon:Link FA
